Consulting Services
Since 1975
Engineering

Site Navigation
Project Quick Links
Projects will
be updated on an ongoing basis. When first
added, new projects will be indicated as shown:
![]()
Projects that
are currently underway are indicated "ongoing" as shown:
![]()
Links to Projects by Year
|
|
| 2009 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
P2900s |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2008 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
P2813 |
DEMAND MODEL CLIENT: ATCO DATE: 2008 DESCRIPTION: A preliminary design for the demand model from gas storage caverns in northern Alberta was developed. The model is to utilize the results of a statistical analysis of the volume flows correlated with ambient temperatures at roughly 80 gate or supply stations. Its purpose is to be able to predict the likely gas demand from the cavern for predicted user population under very cold winter temperatures. The project consisted of the review of previous work, data analysis, and a preliminary model design. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
P2809 |
MOLIKPAQ HAZEER CLIENT: Sakhalin Energy Investment Corporation (SEIC) DATE: 2008-- DESCRIPTION: As Sakhalin Energy Investment Corporation (SEIC) requested to provide an on-site EER hazard evaluation analysis at the Molikpaq, which is part of the Sakahin II development. The work under this project, to date, has consisted of review of data, preliminary assessment of the existing EER system, and the development of logistics for the conduct of the HAZEER. Due to administrative reasons, the project has not proceeded further in 2008. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
P2805 |
ICETECH 2008 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE & EXHIBITION WRAP UP |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
P2803 |
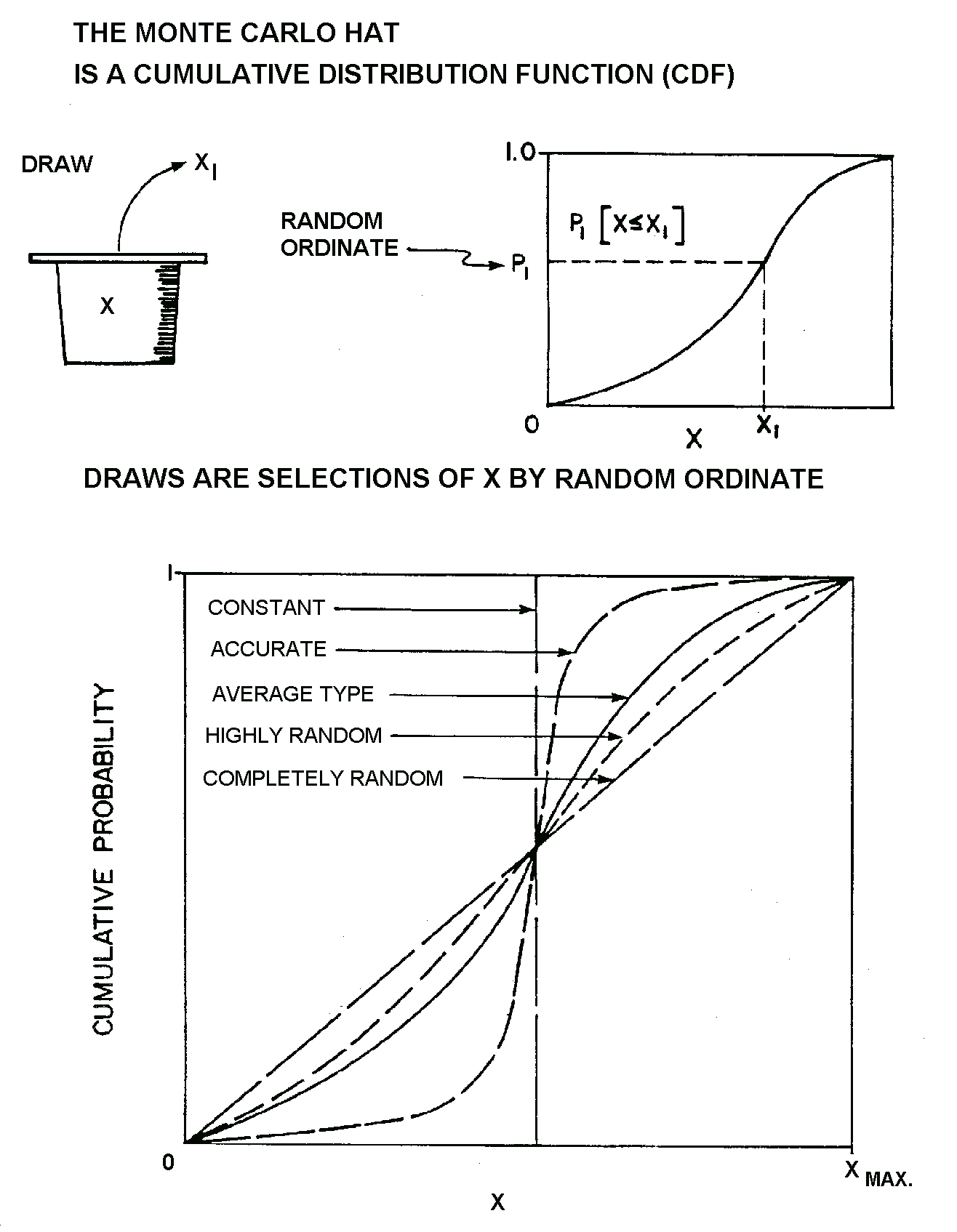
ALBERTA CLIPPER CLIENT: Enbridge DATE: 2008 DESCRIPTION: Provision of support risk services during the design and construction stages of a major crude oil pipeline from the Edmonton area to a location in southern Manitoba, south of St. Leon, where it crosses into the United States. Support services have included probabilistic analysis of various bid components and bids for construction of the various portions of the pipeline, general risk services, and detailed analysis of bids for each of the main segments, utilizing Monte Carlo simulation in order to provide probabilistic distributions of the likely outcomes in economic terms of these bids. The methodology utilized was a risk factor approach in which weighing factors were attributed to all significant factors associated with the likely economic performance of each bidder, to provide a risked cumulative distribution function of the probable capital cost distribution. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
P2802 |
HARDISTY MERCHANT TANKS COST TO COMPLETION RISK CLIENT: Enbridge DATE: 2008 DESCRIPTION: In this study Bercha assessed risks to capital costs for a large industrial project. Cost distributions were calculated using selected risk factors, as well as the entire array of risk factors. The analysis was conducted on the basis of historical performance since the inception of the system, considering various economic factors, to provide a probable capital cost distribution using Monte Carlo simulation. Pertinent conclusions were generated and recommendations offered. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
P2801
|
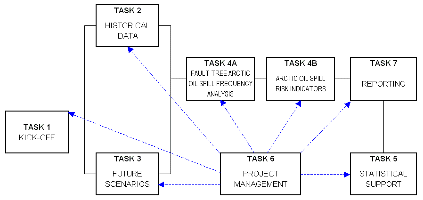
JOINT INDUSTRY PROJECT FEASIBILITY OF ARCTIC INSTALLATION EER CLIENT: ConocoPhillips (Canada) and StatoilHydro (Norway) DATE: 2008---(ongoing) DESCRIPTION: The project consists of the analysis of existing EER systems for Arctic applications, their evaluation, and ranking according to reliability and overall feasibility, and the design and reliability analysis of new EER systems for locations selected by each of the partners. The site-specific analysis consists of the development of two alternative EER system configuration and its reliability analysis using the Bercha Probabilistic Escape, Evacuation, and Rescue Simulator (PEERS) to assess the absolute and relative reliability under a range of site-specific environmental and installation-specific operational and accident conditions. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
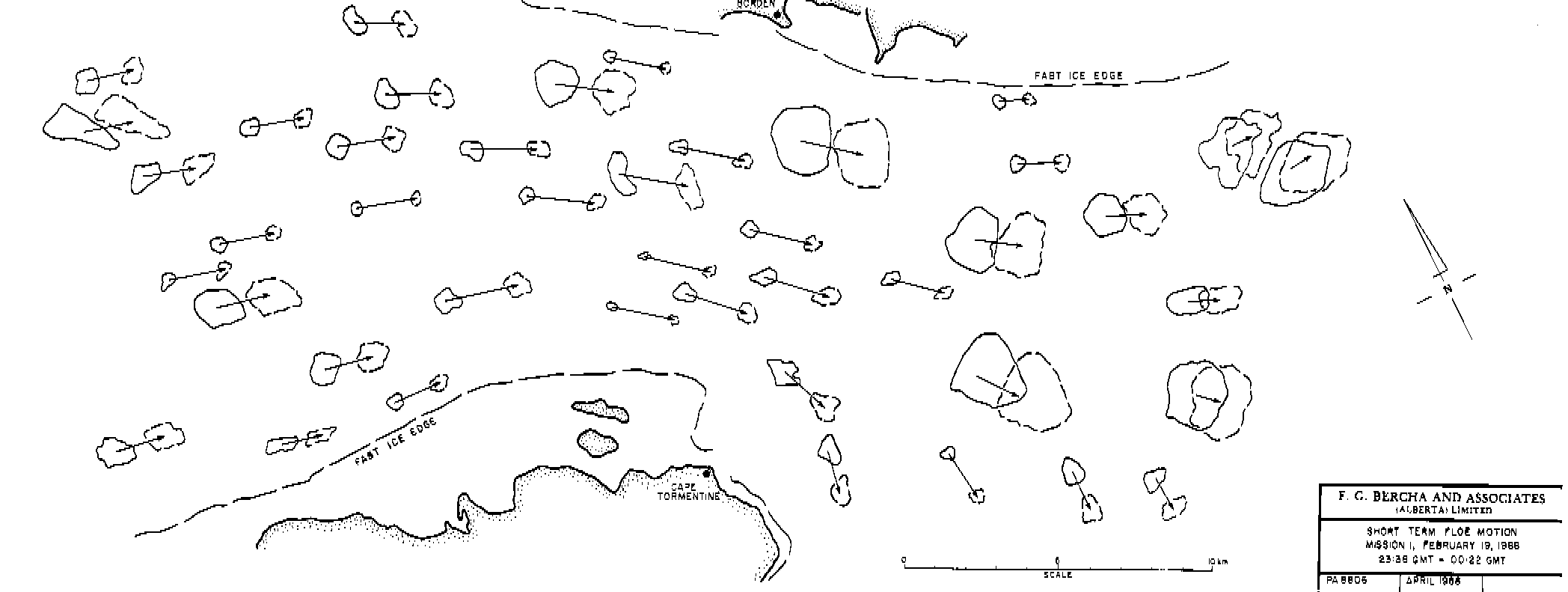
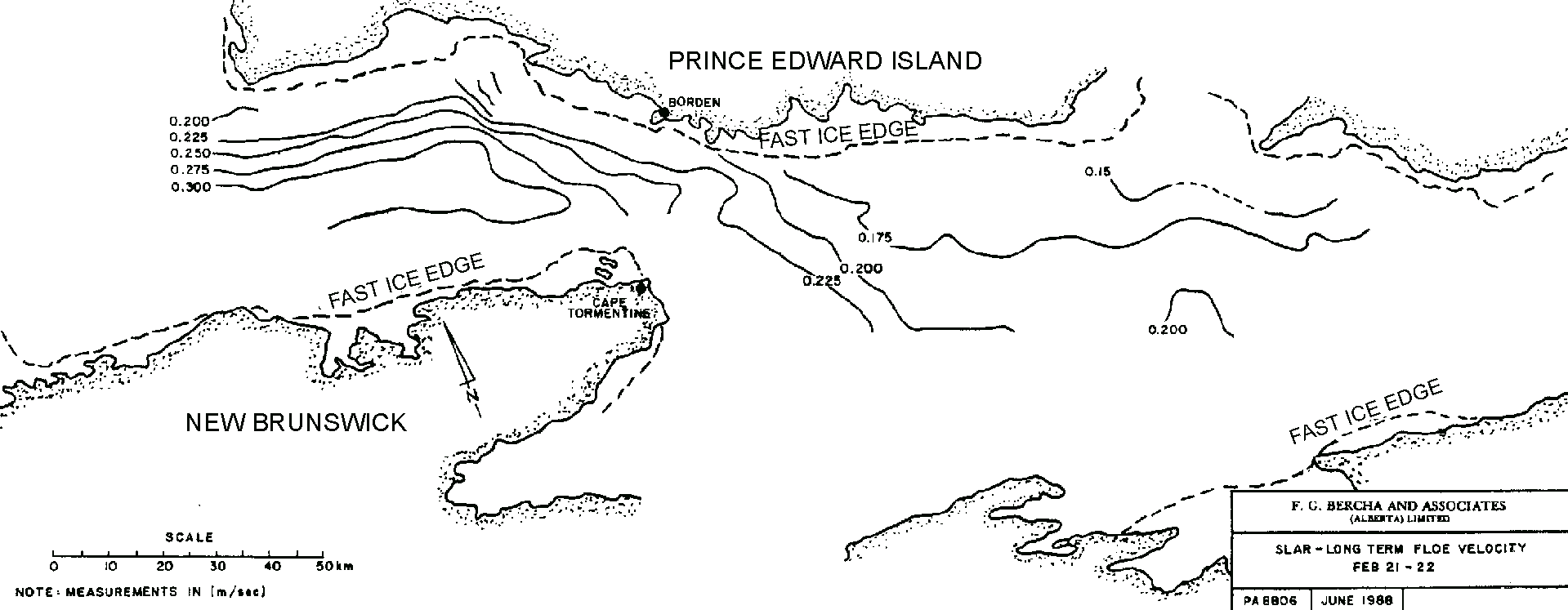
| P2710 |
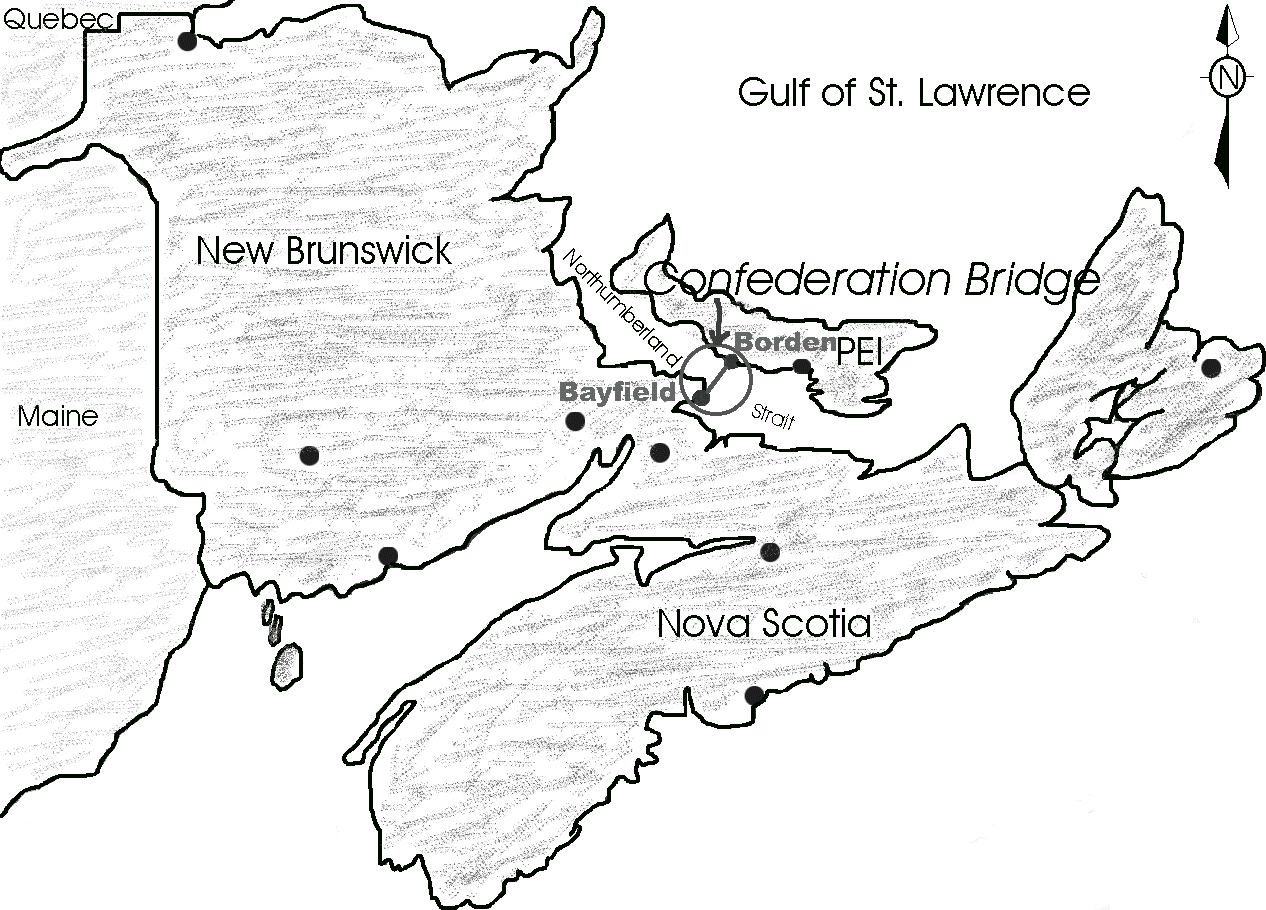
NEW BRUNSWICK PIPELINE EPZ DESIGNATION CLIENT: New Brunswick Pipeline DATE: 2007-2008 DESCRIPTION: An Emergency Planning Zone (EPZ) is an area in the vicinity of a hazardous installation, for which an Emergency Response Plan (ERP) is developed and implemented. The development of the plan requires the designation of an EPZ. In this study, Bercha considered and made recommendations for an appropriate EPZ designation, for which an Emergency Response Plan (ERP) will be developed and implemented. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P2707 |
ARKTOS EER SYSTEM CLIENT: Transportation Development Centre (TDC) of Transport Canada DATE: 2007 Ongoing continuation of projects P2701, P2601, P2501, P2401, P2301, P2201, P2101, and P2001 DESCRIPTION: The Final Report to project P2701, entitled “Escape, Evacuation, and Risk Research Project: Phase III”, summarized the work conducted in the subject area from January 2000 to February 2006, and was published under TP14600E in March 2006. In 2007, additional information and data were obtained on the ARKTOS evacuation system, referred to in Sections 2.2.4 and 2.5 of the Phase III Final Report. Because these data, obtained through both direct experiment and from the manufacturer and various third party sources, provides a better representation of the ARKTOS system and its capability, an Addendum Report was generated under this project P2707. It specifically updated Sections 2.2.4 and 2.5 of the Phase III final report, and provided additional information on the ARKTOS system. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P2705 |
PIPE TESTS CLIENT: Confidential Client DATE: 2007 DESCRIPTION: Bercha provided advice and analysis of the statistical significance of a pipe testing program, including a future test configuration to provide adequate statistical significance on the integrity of pipemill produced line pipe. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Alternative Oil Spill Occurrence Estimators CLIENT: United States Department of the Interior, Minerals Management Service, Alaska DATE: Ongoing continuation of P2407 – contracted to Year 2010 DESCRIPTION: Oil spill occurrence estimates were generated for several expected future oil and gas development scenarios (including exploration, production, and abandonment) in the Alaska Offshore Continental Shelf (OCS) lease sale regions. Because sufficient historical data on offshore oil spills for these regions do not exist, an oil spill occurrence model based on fault tree methodology was developed and applied. Using the fault trees, base data from the Gulf of Mexico including the variability of the data, were modified and augmented to represent expected Arctic offshore oil spillage frequencies. Three principal spill occurrence indicators, as follows, were quantified: § Spill frequency § Spill frequency per barrel produced § Spill index, the product of spill size and spill frequency
These indicators were quantified for the following spill sizes:
Quantification was carried out for each future year for principal development scenarios, with a range of development parameters, in duration up to 40 years. In addition, a comparative scenario for non-Arctic locations was formulated and analyzed for oil spill occurrence. Generally, it was found that the non-Arctic spill indicators were likely to be significantly higher than those for similar scenarios in the Arctic. The computations were carried out using a Monte Carlo process to permit the inclusion of estimated uncertainties in the base and scenario data and Arctic effects. A wide range of details for each scenario was generated, including the following: § Expected time history of spill occurrences over the scenario life. § Spill occurrence variations by spill volumes in the above spill size ranges. § Spill occurrence variation by spill cause such as boat anchoring or ice gouging. § Spill occurrence contribution from each main facility type, including pipelines, platforms, and wells. § Comparison of spill occurrence predictions between Arctic and non-Arctic scenarios. § Life of field averages of spill occurrence estimators. § The variability in the results due to uncertainties in the inputs was expressed as cumulative distribution functions and statistical measures.
In the final report, a detailed description of the methodology, results, and conclusions and recommendations will be given, as well as a section on limitations of the study. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P2701 |
ESCAPE, EVACUATION,
AND RESCUE (EER) R&D - PHASE
III-B
Ongoing continuation of projects P2601, P2501,
P2401, P2301, P2201, P2101, and P2001 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2006 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
P2615
|
ICETECH 2008 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE & EXHIBITION on
Performance of Ships and Structures in Ice CLIENT: Society of Naval Architects and Marine Engineers (SNAME) DATE: July 20-23, 2008 (ongoing) DESCRIPTION: ICETECH-08 is set for July 2008 in Banff. Dr. Bercha again chairs the Organizing Committee, an international conference and exhibition on performance of ships and structures in ice to be held in Banff, Alberta, Canada, July 2008. The theme and subject areas of the conference complement and derive impetus from the current rapid growth of development and associated resurging interest in oil and gas exploration and production in Arctic offshore regions. For updated information and conference details, visit the conference website: www.icetech08.org. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P2610 |
ICETECH 2006 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE & EXHIBITION WRAP UP |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P2603 |
GENERAL REGULATORY ADVICE CLIENT: ATCO Pipelines DATE: 2006 DESCRIPTION: Bercha, together with a legal firm, reviewed the significance of various CSA Z662 Class provisions, and assisted in a pragmatic interpretation of these within the context of ATCO natural gas transmission lines in different class locations. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P2602 |
UNDER BALANCED DRILLING INDUSTRY GUIDELINES CLIENT: Canadian Association of Drilling Contractors (CAODC) DATE: 2006 DESCRIPTION: Bercha assisted in the development of an under balanced drilling industry recommended practice (IRP) by facilitating various hazard identification sessions together with members of the IRP-24 sub-committee. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P2601 |
ESCAPE,
EVACUATION, AND RESCUE (EER) R&D - PHASE III-B CLIENT: Transportation Development Centre, Transport Canada DATE: 2006 DESCRIPTION: As part of EER Phase III, Bercha carried out focused R&D leading to the development of performance-based standards and guidelines for the offshore industry. Project P2601 is the continuation of and completion of the work started under project number P2501. Please refer to P2501 for more information. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2005 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P2507 |
ALTERNATIVE OIL SPILL OCCURRENCE ESTIMATORS AND THEIR
VARIABILITY FOR THE CHUKCHI SEA - FAULT TREE METHOD DESCRIPTION: Oil spill occurrence estimates were generated for several expected future oil and gas development scenarios (including exploration, production, and abandonment) in the Chukchi Sea Offshore Continental Shelf (OCS) lease sale regions. Because sufficient historical data on offshore oil spills for these regions do not exist, an oil spill occurrence model based on fault tree methodology was developed and applied. Using the fault trees, base data from the Gulf of Mexico including the variability of the data, were modified and augmented to represent expected Arctic offshore oil spillage frequencies. Three principal spill occurrence indicators, as follows, were quantified: § Spill frequency § Spill frequency per barrel produced § Spill index, the product of spill size and spill frequency
These indicators were quantified for the following spill sizes:
Quantification was carried out for each future year for one principal Chukchi Sea development scenario, with a range of development parameters, in duration up to 39 years. In addition, a comparative scenario for non-Arctic locations was formulated and analyzed for oil spill occurrence. Generally, it was found that the non-Arctic spill indicators were likely to be significantly higher than those for similar scenarios in the Arctic. The computations were carried out using a Monte Carlo process to permit the inclusion of estimated uncertainties in the base and scenario data and Arctic effects. A wide range of details for each scenario was generated, including the following: § Expected time history of spill occurrences over the scenario life. § Spill occurrence variations by spill volumes in the above spill size ranges. § Spill occurrence variation by spill cause such as boat anchoring or ice gouging. § Spill occurrence contribution from each main facility type, including pipelines, platforms, and wells. § Comparison of spill occurrence predictions between Arctic and non-Arctic scenarios. § Life of field averages of spill occurrence estimators. § The variability in the results due to uncertainties in the inputs was expressed as cumulative distribution functions and statistical measures.
In the final report, a detailed description of the methodology, results, and conclusions and recommendations is given, as well as a section on limitations of the study. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P2506 |
EXPERT
TESTIMONY AND TECHNICAL SUPPORT CLIENT: Confidential Client DATE: 2005 DESCRIPTION: Bercha assisted in the development of technical evidence for various aspects of the client's pipeline integrity and operation. The work covered interpretations of regulatory provisions in the United States and international regime as well as review of specific operating and design procedures. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
P2504 |
RED DEER PIPELINE SYSTEM OPTIMIZATION DESCRIPTION: Bercha assisted ATCO in the development and application of a system for ranking the rehabilitation priority of its pipelines. The work included a helicopter and walkabout inspection of the Southern Extension pipeline and meetings with ATCO personnel to discuss possible risk-based approaches to the rehabilitation ranking. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P2503 |
FAULT
TREE
ANALYSIS OF ALBERTA SOUR GAS FACILITIES DESCRIPTION: The Alberta Energy and Utilities Board (AEUB) required a comprehensive frequency analysis of operating sour gas facilities throughout the province. By sour gas facilities under this project, are meant all sour gas well drilling, production well, pipeline, and other facility operations. Other facilities include those not covered by the three specified types of operations and included, but are not restricted to, items such as above grade metering, pig trap, valve, compressor station, and gas plant facilities. These latter facilities are referred to herein as “Other Facilities”. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P2502 |
HIGH CONSEQUENCE AREAS IDENTIFICATION
AND RANKING - A working definition of HCAs is developed - A methodology for identification of the HCAs is defined - An identification of HCAs for the pipeline is conducted - Approaches to HCA mitigation are developed. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
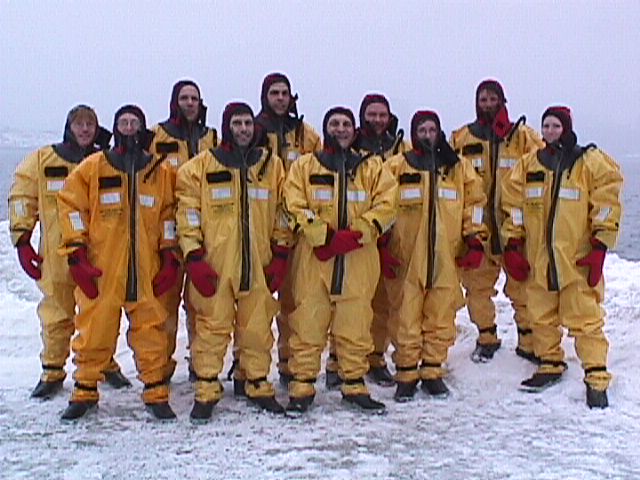
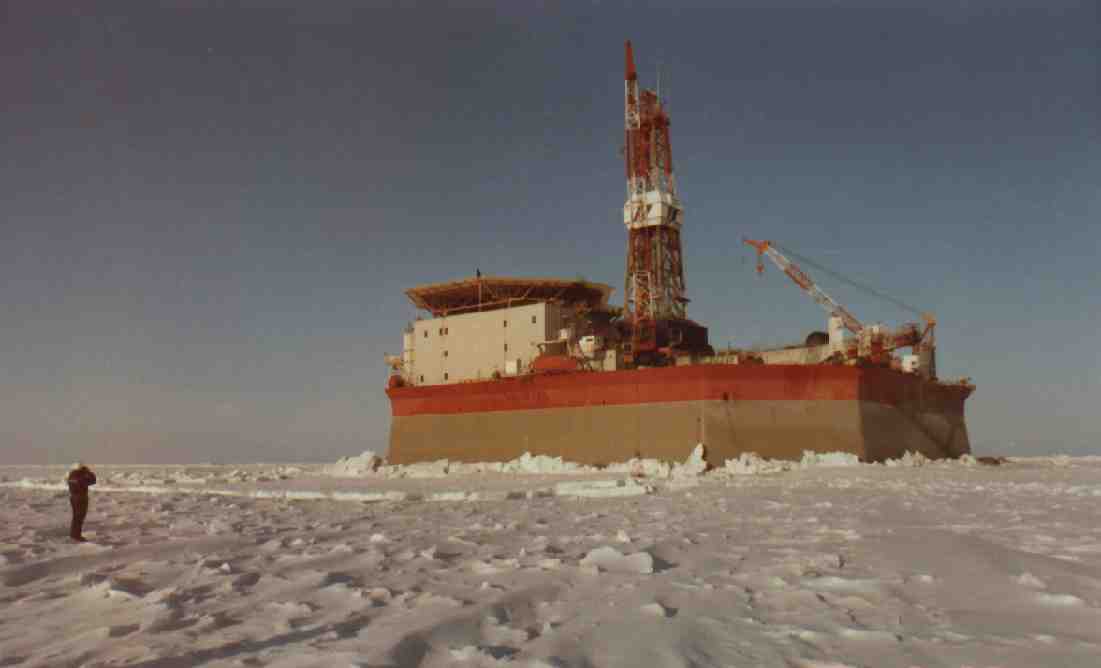
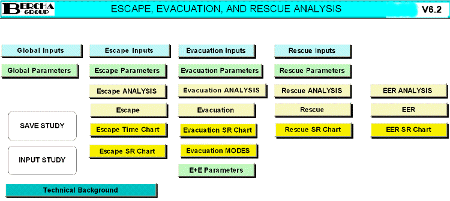
|
ESCAPE,
EVACUATION, AND RESCUE (EER) R&D - PHASE III-B
EER R&D
projects Phases I, II, and III-B are described under project
numbers: P2001, P2101,
P2201, P2301, and
P2401. Photos below are from all Phases of
the project. More information can also be found on our
PBS
downloads
page.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
P2408
|
CRUDE OIL
PIPELINE INCIDENT, REGULATION, AND PRACTICE REVIEW CLIENT: Confidential Client DATE: 2004 DESCRIPTION: A confidential review of information relevant to the location of hydrocarbon pipelines, with specific emphasis on crude oil pipelines, in relation to urban centres of population was carried out. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ALTERNATIVE OIL SPILL OCCURRENCE ESTIMATORS FOR THE BEAUFORT SEA
- FAULT TREE METHOD - Extension to Include Variability of
Non-Arctic Effects
DATE: 2005
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P2406 |
SOUR GAS
BLOWOUT IGNITION STUDY CLIENT: Alberta Energy and Utilities Board (EUB) DATE: 2004 DESCRIPTION: The requirements for blowouts occurring during the drilling of critical sour gas wells is the ignition of the blowout in order to reduce the risk from H2S through combustion to SO2. However, there is not currently a clear understanding of exactly how long it will take and how reliable it will be to ignite the blowout under real life threatening conditions. Bercha has developed software that takes into account human performance under life threatening conditions in its studies of onshore and offshore emergencies. Under this contract, Bercha has been retained to simulate both the time and the reliability of ignition of sour gas blowouts under different weather and operational and accident conditions. Results will be used as part of the requirements for development of emergency planning zones at critical sour gas wells. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P2405 |
QUALITATIVE RISK ASSESSMENT OF HALIFAX HARBOUR NATURAL GAS
PIPELINE CROSSING OPTIONS CLIENT: Heritage Gas DATE: 2004 DESCRIPTION: A risk assessment was carried out in support of Heritage Gas feasiblity studies on construction of a pipeline connecting the Dartmouth side of Halifax Harbour (where natural gas is supplied from the Maritimes and Northeast Pipelines Halifax Lateral), across the Halifax Harbour Narrows to terminate on the Halifax Peninsula within the City of Halifax. Preliminary estimates indicated that an NPS 10 pipeline with an MOP of 275 psig, approximately 1 km in length, would provide the required capacity. The Bercha risk assessment focused on two crossing options: a. Under-Harbour Crossing using Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD); b. Suspended Bridge Crossing (SBC) using the Macdonald Bridge. The general objective of the work was to provide Heritage Gas with a comprehensive but high level and qualitative picture of the risk of exposure that would be encountered both during construction and subsequent pipeline operation for the HDD and the SBC crossing options. The assessment addressed the risks in two distinct phases; namely, the construction phase and the operating phase. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P2404 |
REVIEW OF
RISK AND ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENTS FOR THE PROPOSED
CANNONBALL DEVELOPMENT CLIENT: Environmental Management Authority, Government of Trinidad and Tobago DATE: 2004 DESCRIPTION: Bercha International Inc. was retained through Jacques Whitford for the review of documents supporting an application to the Environmental Management Authority of the Government of Trinidad and Tobago. This application was made by British Petroleum for a Certificate of Environmental Clearance (CEC) to develop the oil and gas reserves of the Cannonball Field that is located in the South East Galeota Block, 60km offshore the East Coast of Trinidad. Essentially, the proposed project would contain both offshore and onshore segments. The offshore segment would consist of a proposed wellhead protector platform, and a new 26” pipeline running from the platform to an existing pipeline to an onshore facility. The onshore development would consist of a modification of an existing onshore gas processing facility to increase its capacity. Bercha’s work consisted of reviewing the hazard and consequence assessment, a quantitative risk assessment, and an environmental impact assessment (EIA)), and assessing the validity and appropriateness of the methodology, running check calculations, and making recommendations in relation to the methodology and in relation to the results. The standards applied in the review were those standards normally applied to similar developments in western countries such as Canada and the USA. Generally, the methodology of the onshore facility QRA is compatible with existing standards, while no QRA was done for the offshore segment. The EIA is compatible with standards for preliminary EIA with respect to public and environmental risks. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P2403 |
QUANTITATIVE RISK ASSESSMENT OF THE SHELL MOOSE MOUNTAIN TO
JUMPING POUND INTERCONNECT PIPELINE CLIENT: Shell Canada Limited DATE: 2004 DESCRIPTION: Bercha performed a risk assessment of Shell’s proposed Interconnect Pipeline (IP) system, from the Moose Mountain Compressor Station (MMCS) to the Jumping Pound Gas Plant (JPGP). The goal of the work was to evaluate the risks associated with operating the proposed interconnect pipeline. The work was used to support an EUB application for the construction of the proposed interconnect pipeline and assist in the Shell risk management program development for the proposed system. A quantitative risk assessment (QRA) was conducted including consideration of the engineering and operational parameters of the proposed project within the context of the current location. The primary focus of the risk assessment was quantification of acute risks to the public. The key results of the work were estimates of individual and collective risks to the public. Both individual and collective risks were found to be sufficiently low to be considered acceptable. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P2402 |
RISK
ASSESSMENT OF PROPOSED ATCO PIPELINE RELOCATION CLIENT: ATCO Pipelines, Edmonton, Alberta DATE: 2004 DESCRIPTION: ATCO Pipelines proposed to relocate an NPS-4 high-pressure sweet natural gas pipeline along a 6-km segment of Highway 40 in the vicinity of the Smoky River Mine. A risk analysis was carried out to support engineering and management decisions and the application to the AEUB for licensing of the project. The principal results of the risk assessment were individual specific risk (ISR) transects describing the risks from the proposed pipeline to public and worker personnel in its vicinity. Risk mitigation measures were also investigated qualitatively, and several key risk mitigation measures were recommended. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P2401 |
ESCAPE,
EVACUATION, AND RESCUE (EER) R&D - PHASE III-A CLIENT: Transportation Development Centre, Transport Canada DATE: 2004-2005 DESCRIPTION: As part of EER Phase III, Bercha will carry out focused R&D leading to the development of performance-based standards and guidelines for the offshore industry. The goal of the program is to develop a prioritized and focused R&D program specific to EER, which will lead to the implementation of performance standards for the offshore industry. The Canadian Petroleum Boards have indicated that they will administer the Standards and implement them as Board Guidelines under the Accord Act. The Boards support the continuation of the EER research program and in parallel, the Boards, in co-operation with industry, have initiated a process to review the draft standard by the regulator. The results of this work will provide the rationale for the Regulators to evaluate design standards for EER systems employed in the offshore industry. The performance-based guidelines will address all relevant Human Factors/Ergonomic considerations with respect to the usability of the systems, training and other associated elements. Current work which is underway or has been carried out to support the R&D program under Phase III-A includes the following:
EER R&D projects Phases I, II, and III-B are described under project numbers: P2001, P2101, P2201, P2301, and P2501. More information can also be found on our PBS downloads page. |
| P2315 |
ICETECH-06 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE &
EXHIBITION CLIENT: n/a DATE: July 16-19, 2006  DESCRIPTION: Dr. Bercha chaired the Organizing Committee for ICETECH 2006, an international conference and exhibition on performance of ships and structures in ice held in Banff, Alberta, Canada, July 16-19, 2006. The theme and subject areas of the conference complemented and derived impetus from contemporary rapid growth of development and associated resurgence of interest in oil and gas exploration and production in Arctic offshore regions. Updated information and conference details were available on the conference website. |
||||
|
|
ISO ARCTIC
STRUCTURES STANDARD TP2a – RELIABILITY
 CLIENT: International Standards Organization DATE: 2004--- DESCRIPTION: Dr. Bercha chairs the ISO Technical Panel 2a drafting this Standard. ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of national standards bodies (ISO member bodies). The work of preparing International Standards is carried out through ISO technical committees. International Standard TP 2a was prepared by WG8 AS 25B Arctic Structures, Subcommittee TP 2a Reliability. TP2a is part of a series of standards for arctic offshore structures.
|
||||
|
|
WG8
TECHNICAL PANELS ISO 2G8 AS25B ARCTIC STRUCTURES STANDARD -
ESCAPE, EVACUATION, AND RESCUE - 8B
 CLIENT: International Standards Organization DATE: 2004--- DESCRIPTION: Dr. Bercha is a member of the ISO Technical Panel 8b drafting this Standard. ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of national standards bodies (ISO member bodies). The work of preparing International Standards is carried out through ISO technical committees. International Standard TP 8b was prepared by WG8 AS 25B Arctic Structures, Subcommittee TP8b Escape, Evacuation, and Rescue. TP8b is part of a series of standards for arctic offshore structures.
|
||||
| P2311 |
RISK RISK RE-ASSESSMENT OF SHELL MOOSE MOUNTAIN MAINLINE BETWEEN MOOSE MOUNTAIN AND WHISKEY CREEK COMPRESSOR STATIONS
CLIENT: Shell
Canada Limited DATE: 2003 |
||||
| P2310 |
LINE 96
LEAK DETECTION SYSTEM (LDS) REVIEW
|
||||
| P2308 |
QUATAR
FACILITY FREQUENCY ESTIMATES CLIENT: Jacques Whitford Environmental Limited DATE: 2003 DESCRIPTION: As part of a facility assessments, Bercha Group conducted frequency estimates for the following: - Total Plant Emergency Depressurization to Flare - Emergency Flare Flameout - Marine Terminal Fire or Explosion - Tanker Fire and Explosion During Loading |
||||
| P2307 |
SHELL
MOOSE MOUNTAIN MAINLINE RISK RE-ASSESSMENT CLIENT: Shell Canada Limited DATE: 2003 DESCRIPTION: Shell Canada Limited (Shell) has retained the Bercha Group (Bercha) to perform a risk re-assessment of the Moose Mountain Mainline (MMM) system, from the Moose Mountain Compressor Station to the Imperial Oil Quirk Creek Gas Plant (QCGP). The goal of the work is to re-evaluate the risks associated with operating the existing pipeline to its full design capacity, beyond the present operational restrictions associated with the existing conditions that act to cap the operating H2S release volumes to values well below Alberta Energy and Utilities Board (EUB) license values. It is anticipated that the work will be used to support an EUB application for ‘review and variance’ of the supplemental conditions. |
||||
| P2306 |
GAS
RESOURCES & CONCEPTUAL DEVELOPMENT WITHIN MUSKWA-KECHIKA
MANAGEMENT AREA, NE BRITISH COLUMBIA CLIENT: APA Petroleum Engineering DATE: 2003 DESCRIPTION: Bercha work constituted part of APA’s development application for regulatory assessment and approval for a proposed project within the Muskwa-Kechika Management area. Bercha carried out a detailed risk analysis, studying facility risks to public safety and the environment. Bercha work also generated project-specific public safety and environmental risk mitigation measures, and contributed to the Environmental Impact Statement (EIS). |
||||
| P2305 |
HAZARD
ANALYSIS FUNDAMENTALS AND APPLICATIONS CLIENT: Plains Marketing Canada DATE: 2003 DESCRIPTION: This two-day training course, conducted by Dr. Bercha, focused on hazard analysis fundamentals and applications. The program included technical theory as well as practical experience through use of Hazop software, enriched through guided study including application of Hazop software on select case studies. |
||||
| P2304 |
SHELL
MOOSE MOUNTAIN RISK RE-ASSESSMENT CLIENT: Shell Canada Limited DATE: 2003 DESCRIPTION: Shell Canada Limited (Shell) was evaluating a line looping project for the canyon section of the existing Moose Mountain infield Gas Gathering System. Shell retained the Bercha Group (Bercha) to perform a risk re-assessment of the Moose Mountain Infield Gas Gathering System based on the proposed line looping design basis. The re-assessment considered the impact of the five planned future wells that will be tied into this pipeline system, based on a range of potential well volumes and compositions. The purpose of the risk re-assessment is to provide support for engineering and design functions and to support an Energy and Utilities Board (EUB) energy development application expected to be filed in the near future. The figures below highlight some of the unique aspects of this area. |
||||
| P2303 |
BLUE
ATLANTIC PROJECT ONSHORE FACILITY RISK ASSESSMENT CLIENT: Jacques Whitford Environment Limited DATE: 2003 DESCRIPTION: Bercha carried out a quantitative risk assessment of proposed onshore facilities. Generally, the work was subdivided into two principal risk analytic components as follows: Risk analysis of the pipelines, and a high-level risk analysis of the proposed gas plant. Because of their location in a rural populated area, the pipeline risk assessment was to be carried out to a relatively high level of detail and comprehensive quantification. The gas plant, however, was restricted in risk analysis scope to a much more general level, with focus on quantitative risk assessment on major releases with potential offsite damaging effects. |
||||
| P2302 |
SD283
HUMBER PLACE SUBDIVISION - SAFETY ASSESSMENT CLIENT: TransCanada Pipelines Limited DATE: 2003 DESCRIPTION: Bercha conducted a review of the risk and safety implications of two alternative subdivision configurations in the vicinity of the subject pipeline. Tasks included information review, conduct of a quantitative accident probability analysis, and generation of conclusions and recommendations on the preferred pipeline route. |
||||
| P2301 |
ESCAPE,
EVACUATION, AND RESCUE (EER) R&D PHASE 3 CLIENT: Transportation Development Centre, Transport Canada DATE: 2003-- DESCRIPTION: As part of EER Phase III, Bercha will carry out focused R&D leading to the development of performance-based standards and guidelines for the offshore industry. Work carried out under Phases 1 and 2 (P2101 and P2201) is the foundation for Phase 3. The goal of the program is to develop a prioritized and focused R&D program specific to EER, which will lead to the implementation of performance standards for the offshore industry. The Canadian Petroleum Boards have indicated that they will administer the Standards and implement them as Board Guidelines under the Accord Act. The Boards support the continuation of the EER research program and in parallel, the Boards, in co-operation with industry, will initiate a process to review the draft standard by the regulator. The results of this work will provide the rationale for the Regulators to evaluate design standards for EER systems employed in the offshore industry. The performance-based guidelines will address all relevant Human Factors/Ergonomic considerations with respect to the usability of the systems, training and other associated elements. EER R&D projects Phases I, II, and III-B are described under project numbers: P2001, P2101, P2201, P2401, and P2501. More information can also be found on our PBS downloads page. |
| P2204 |
STATISTICAL AND NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF OIL SPILL PERSISTENCE ON
OPEN WATER CLIENT: On Subcontract to: S.L. Ross Environmental Research Ltd., Ottawa, Ontario, Canada DATE: 2003 For: U.S. Department of the Interior, Minerals Management Service, Alaska Outer Continental Shelf Region DESCRIPTION: This project was carried out and reported by Bercha International Inc. (Bercha), on subcontract to S.L. Ross Environmental Research Limited (SLR) the prime contractor to MMS for the project “Persistence of Crude Oil Spills on Open Water”. The objective of the project is to study the relationships between spill persistence and spill size, and to refine the spill persistence and size relationship in terms of other variables while providing possible predictive relationships such as cumulative distribution functions. Essentially, the approach utilized by Bercha following receipt of the spill data from SLR, was to inspect the data for possible approaches, identify a series of statistical and numerical methods which could be used to study the relationships among the principal data variables, apply these methods, select the most statistically significant approaches, and further utilize these approaches to generate certain predictive algorithms and results. |
| P2203 |
RISK AND
COST BENEFIT ANALYSIS OF UTILITY CROSSINGS OF ROADS |
| P2202 |
PUBLIC
SAFETY ASSESSMENT OF TWO ALTERNATE SUBDIVISION CONFIGURATIONS IN
THE VICINITY OF TCPL NATURAL GAS TRANSMISSION PIPELINES CLIENT: TransCanada Pipelines DATE: 2002 DESCRIPTION: An assessment of the risk and safety implications was carried out for two alternative subdivision configurations in the vicinity of the subject pipeline. The study includes: (1) review of pertinent information and data, (2) conduct of a quantitative accident probability analysis, and (3) Option recommendation based on study results. The two subdivision configuration options considered were: (a) Option 1 - TransCanada ROW located in stand-alone corridor behind housing, and (b) Option 2 - TransCanada ROW located in residential road median in front of housing. The methodology included the use of fault trees. |
| P2201 |
ESCAPE,
EVACUATION, AND RESCUE (EER) R&D PHASE 2
EER R&D projects Phases I, II, and III-B are described under project numbers: P2001, P2101, P2301, P2401, and P2501. More information can also be found on our PBS downloads page. |
| P2111 |
GAS
DEMAND COINCIDENCE FACTOR ANALYSIS |
||||
| P2110 |
NEEPAWA PTH 16 ALTERNATIVE ROUTE RISK ASSESSMENT
CLIENT: NDL DATE: 2001-2002 DESCRIPTION: In order to support planning and management decisions for alternate configurations of Highway #16 within the City of Neepawa, a detailed risk assessment for the existing configuration and alternative configurations was carried out. A risk model was developed based on five-year historical accident data for the existing configuration, and extended to consider two options; namely, a divided highway through town, and the existing undivided highway together with a bypass route. Risks were expressed as accident probabilities of three principal categories; those involving property damage, injuries, and fatalities. Results were provided in tabular and graphical format together with recommendations on risk mitigation. |
||||
| P2107 |
INTERIM PROTOCOLS ON DISPERSION MODELING AND RISK ASSESSMENT
CLIENT: Alberta Energy and Utilities Board DATE: 2001-2002 DESCRIPTION: In this joint project with M.J. Zelensky of Public Safety and Air Quality Management, the Bercha Group provided specialized expertise on frequency and risk assessment aspects of sour gas safety. The project entailed the development of a protocol applicable uniformly to all sour gas developments in Alberta, including wells, pipelines, and facilities. A sequence of steps involving preliminary risk screening followed by quantitative risk assessment was identified and the primary benchmarks and methodologies for each of the steps were set out in the interim protocol together with technical appendices thereto giving quantitative information on appropriate parameters to be utilized as inputs to the risk assessments. |
||||
| P2106 |
RAILROAD RIGHT OF WAY PIPELINE EASEMENT STUDIES
CLIENT: Brown, Winfield, and Cansoneri, Attorneys, Union Pacific DATE: 2002 - ongoing DESCRPTION: The work under this project consisted primarily of the provision of expert support and testimony by Dr. F.G. Bercha in regard to engineering issues associated with the construction and operation of high-pressure petroleum liquids pipelines within the Union Pacific 1,800-mile railroad right of way. In 1995, when this case was scheduled for trial, Bercha carried out a number of assessments including constructibility and risk analysis studies. This case was reopened in 2002, and supporting evidence and additional testimony by Bercha was provided thereto. |
||||
| P2103 |
CONCEPT SAFETY EVALUATION FOR THE ALMA DEVELOPMENT PROJECT
CLIENT: Sable Offshore Energy Inc. (SOEI), Halifax, NS DATE: 2001 DESCRIPTION: A Concept Safety Evaluation (CSE) of the conceptual design of the Alma development project was carried out. The work included data assimilation, general hazard identification, qualitative and quantitative risk assessment (QRA), review of safety and EER systems, and the generation of conclusions and recommendations. A range of hazards was considered in the risk assessment. This Concept Safety Evaluation for a development offshore Nova Scotia is regulated by the Nova Scotia Petroleum Directorate, and, as such, is one of the requirements the Directorate sets out as a condition for permits to proceed with such a development. The risks to personnel were the primary focus of the risk evaluation, and both individual and collective risks were evaluated. Individual risks (IR), the actual risks to which individuals with different jobs are exposed, were quantified and compared to Target Levels of Safety (TLS) established for the project. Collective risks (CR) were quantified in terms of Potential Loss of Life (PLL), and assessed within the context of the as low as reasonably practicable (ALARP) principle. The IR TLS’s were as follows: IR below 10-6 is negligible, IR between 10-6 and 10-3 is ALARP, and IR above 10-3 is intolerable. |
||||
| P2102 |
QUANTITATIVE RISK ASSESSMENT OF PROPOSED AES POWER PLANT
CLIENT: AES Calgary ULC DATE: 2001 DESCRIPTION: A quantitative risk assessment (QRA) of the proposed AES Calgary Power Plant was conducted. The risk assessment included consideration of the engineering and operational parameters of the proposed plant within the context of the proposed location parameters. The primary focus of the risk assessment was quantification of acute risks to the offsite public. The scope of the work consisted of the following principal tasks: data acquisition, hazard scenario development, frequency analysis, consequence analysis, risk assessment and acceptability, description of risk mitigation measures, and conclusions and recommendations. The key results of the work are estimates of individual and collective risks to the public. |
||||
| P2101 |
ESCAPE,
EVACUATION, AND RESCUE (EER) R&D PHASE 2
CLIENT: Transportation Development Centre, Transport Canada DATE: 2001 - 2003 DESCRIPTION: Under this project is the development of performance-based standards (PBS) for escape, evacuation, and rescue (EER) for East coast offshore oil and gas installations together with the supporting research. In the first project, the development of the guidelines is carried out, with Bercha providing facilitation, expert personnel, and coordination of a team of offshore safety, human factors, marine operations, and medical experts. The PBS development program is carried out under the guidance of a steering committee comprising Transport Canada, Transportation Development Centre, Canada-Nova Scotia Offshore Petroleum Board, Canada-Newfoundland Offshore Petroleum Board, Canadian Association of Petroleum Producers, and other experts. Bercha is responsible for the drafting and editing of the guidelines and organizing their development, stakeholder consultation, and promulgation. In the second element, there are two supporting research projects, one on human performance under extreme conditions, and the second on the full-scale performance evaluation of specialized evacuation systems. Since experimental data are not available nor can be generated for performance under life threatening conditions, a compendium of all accident anecdotal data, applicable error rate and performance human factors data, and risk and reliability documentation is assembled, reviewed, and transformed into parameters applicable to the operation of the computerized EER probabilistic simulator. In the second subproject, specifically, the Seascape 2000 proprietary system and the PROD or Preferred Orientation and Deployment lifeboat launch system are evaluated. EER R&D projects Phases I, II, and III-B are described under project numbers: P2001, P2201, P2301, P2401, and P2501. More information can also be found on our PBS downloads page. |
||||
| P2013 |
SAFETY OF NORTHERN AND POLAR SHIPPING (SONAPS) - ESCAPE,
EVACUATION, AND RESCUE CLIENT: National Research Council of Canada and European Union, Brussels DATE: 2000-2001 DESCRIPTION: Currently, no adequate standards or technologies exist for the safety of civilian or military ships operating in ice covered waters. Current SOLAS standards do not include requirements for ice reinforcement or ice capability in lifeboats, nor are current launching and evacuation devices suited for Arctic operations. The current project, led by the Bercha Group, addresses the problem of analyzing, developing, and implementing technologies and regulations to assure adequately safe escape, evacuation, and rescue (EER) procedures for a range of common ice conditions from solid ice to broken ice for vessels. The consortium, in addition to the leaders Bercha Group, consist of Scott Polar Research Institute of Cambridge University, Fortun Oil of Finland will provide icebreaker support, the European Union Joint Research Centre from Ispra, Italy, and advisors Umoe Schat-Harding of Oslo, Norway. Currently, the program is in its design phase, with Bercha supported by the National Research Council of Canada, and the other organizations supported by their respective nations. Ultimately, the work will consist of information assimilation, analysis and modeling, conceptual engineering, model testing, and full-scale tests. |
||||
| P2011 |
STUDY OF NATURAL GAS PIPELINE PLACEMENT IN THE RURAL ENVIRONMENT
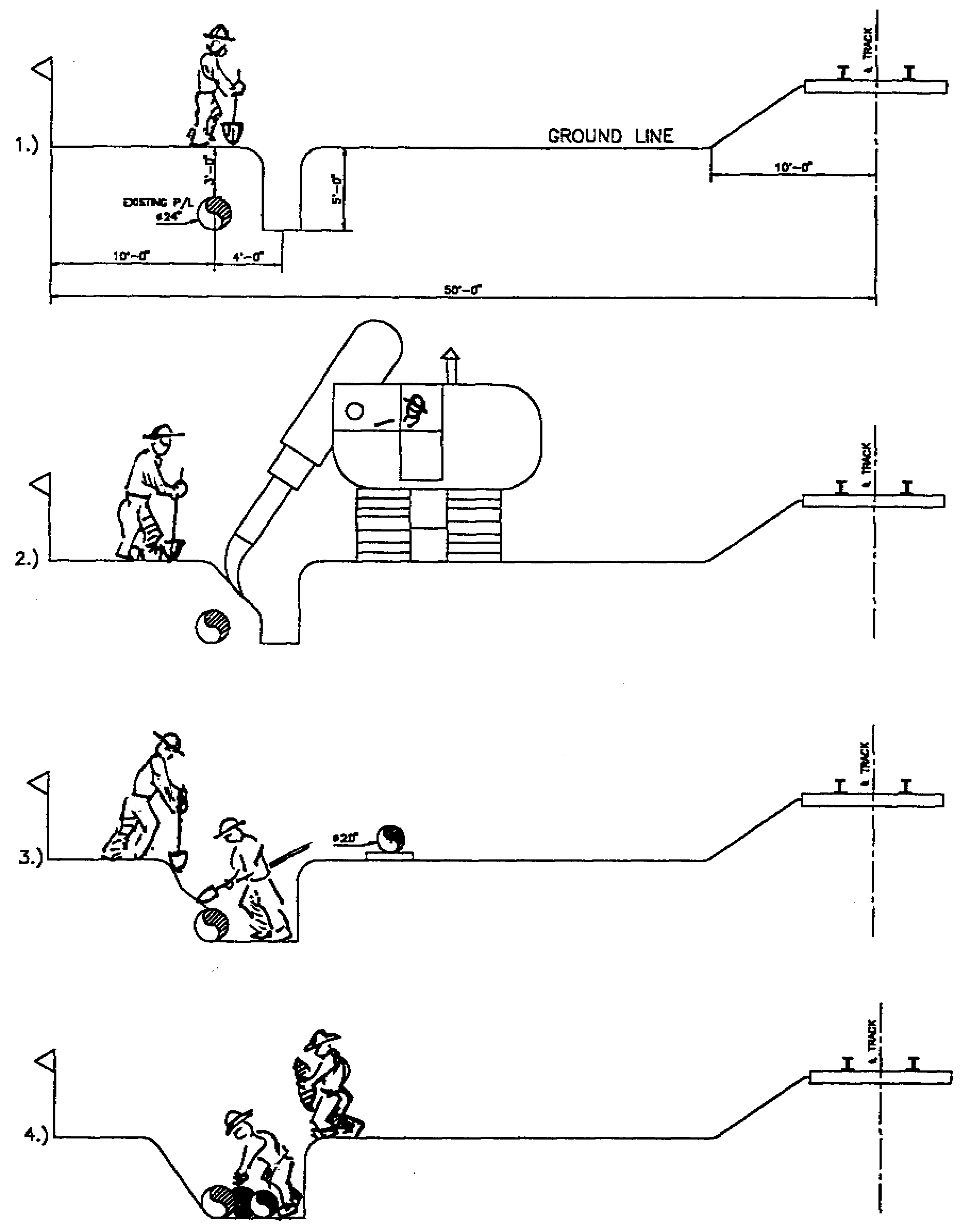
CLIENT: Transportation Association of Canada (TAC) DATE: 2000-2001 DESCRIPTION: The placement and location of hydrocarbon pipelines with respect to road geometries and cross sections can have an effect on the safety of the highway system and its users and adjacent residents, as well as operational and economic impacts on highway maintenance, construction, and modification activities. To assess these risks and impacts, the Transportation Association of Canada (TAC) commissioned Bercha Engineering Limited (Bercha) to conduct an in-depth, comprehensive study directed at generating a qualitative and quantitative understanding of the implications of locating pressurized natural gas pipelines in various locations within rural road right-of-ways. The study covered four primary representative road types together with their variations in ADDT, vehicle speed, and cross section, as well as three representative pipeline sizes and pressure categories for three different pipeline locations. The three pipeline locations consisted of one in the shoulder, one below the ditch, one just inside the edge of the right-of-way, and a fourth control location where the pipeline is away from the effects of the roadway. The method for systematically quantifying the risks to the public, considering the effects of the pipeline-roadway synergy, including effects on the pipeline failure rate as well as consequences of possible failure including ignition by vehicles, was developed and applied to each of the 108 generic cases. Both individual and collective risks and their variations for each of the different combinations were evaluated, and discussed. Similarly, economic impacts, including increases in the unit cost of common maintenance, construction, and reconstruction activities for the road operators were also identified. A series of conclusions and recommendations was generated, including definition of compatible and incompatible combinations of pipeline and location installations in terms of safety, cost, and constructability; various risk and impact mitigation measures to enhance safety and reduce costs; and long-term approaches to optimize the situation. Although previous studies have been done on the use of common utility and transportation corridors, no comprehensive quantitative assessment of risks and economic impacts for representative combinations of road and pipeline characteristics has appeared previously, resulting in a significant volume of new observations and information available from the work reported herein. The report can be purchased online at the TAC bookstore. |
||||
| P2010 |
ALTERNATIVE OIL SPILL OCCURRENCE ESTIMATORS FOR THE BEAUFORT AND
CHUKCHI SEAS Click on the thumbnails to view enlarged images.
|
||||
| P9709 |
SAFETY CASE FOR THE SABLE OFFSHORE ENERGY PROJECT
CLIENT: Sable Offshore Energy Project DATE: 1997 - 2001 DESCRIPTION: The Bercha Group wa s the prime contractor for the Concept Safety Evaluation and subsequent safety case of the Sable Offshore Energy Project, providing overall project management, conducting the CSE for all onshore facilities, as well as selected segments of the offshore facilities including the Straits of Canso crossing and ship/collision probability assessments associated with the offshore platforms. Bercha conducted the QRA through a systematic sequence of data assimilation, hazard scenario development, frequency evaluation, consequence assessment, risk analysis, risk acceptability evaluation, risk mitigation measure development, and resultant or residual risk assessment. For each of the principal facility components, including marine pipeline, gas processing plant, NGL Pipeline, NGL Fractionation Plant, and NGL Products Distribution Terminal. Subsequent QRAs relating to the project were conducted by Bercha in the area of Statia Marine Terminal risk assessment, fire and explosion consequence analysis, offshore escape evacuation and rescue studies, several HAZOP and HAZ-IDs, and general risk management and safety program development for the safety case associated with the project. |
||||
|
P2009 .02 |
TR
AIR BREATHABILITY FOR THEBAUD CLIENT: Sable Offshore Energy Project, Halifax, NS DATE: 2000, August DESCRIPTION: A probabilistic analysis of breathable atmosphere in Thebaud TR for various complements was carried out. |
||||
|
P2009 .01 |
THEBAUD MEG SYSTEM WHAT-IF HAZOP CLIENT: Sable Offshore Energy Project, Halifax, NS DATE: 2000, July DESCRIPTION: A HAZOP for the Thebaud Monoethylene Glycol (MEG) pipeline injection system was conducted. The methodology used was a knowledge-based What-If HAZOP for two principal nodes comprising the system. |
||||
| P2006 |
REVIEW OF CONSEQUENCE MODELS FOR HYDROCARBON PIPELINES
CLIENT: Canadian Energy and Pipeline Association (CEPA) DATE: 2000-2001 DESCRIPTION: The CEPA Pipeline Integrity Working Group project includes a review of consequence models applicable to the modeling of hazard effects resulting from a variety of pipeline failures. Over the last few years, with the vast increase in micro-computing capability together with extensive improvements in software computational, input-output, graphic, and export capabilities, a considerable proliferation of consequence and risk models applicable to the petrochemical industry has taken place. Whereas up to the late-1970s and early-1980s, models were typically in Fortran, operated in a DOS-based environment, with the advent of the Windows environment and powerful computational, programming, and graphic capabilities, a variety of multipurpose and specialized consequence models applicable to assessing hazard effects from pipeline failures have become available. These models vary significantly in their comprehensiveness, user friendliness, and cost, to mention only a few factors. Accordingly, a systematic compilation of data on these models together with a comparative assessment based on industry established standards was carried out. |
||||
| P2003 |
EPCOR ROSSDALE POWER PLANT MODIFICATION RISK ANALYSIS
CLIENT: EPCOR Power Generation Inc., Edmonton, Alberta DATE: 2000 DESCRIPTION: A quantitative risk assessment (QRA) of the proposed EPCOR Rossdale Power Plant modification was conducted. The risk assessment included consideration of the engineering, construction, and operational parameters of the existing and modified plant. The primary focus of the risk assessment was quantification of acute risks to the public. |
||||
| P2002 |
INVESTIGATION OF RISKS TO AND FROM HAZARDOUS FACILITIES ADJACENT
TO THE HALIFAX NATURAL GAS LATERAL PIPELINE
CLIENT: Maritimes and Northeast Pipelines DATE: 2000 DESCRIPTION: The work, a permit condition mandated by the National Energy Board, involves the assessment of interactive risks between the Halifax Lateral, a high-pressure natural gas pipeline, and adjacent hazardous facilities. These hazardous facilities include liquid propone storage tanks, the Air Liquide processing plant, various crude oil and other chemical storage facilities, and railway facilities including a railway yard and several main line level crossings at locations where the pipeline is located in the railway right-of-way. The work consisted of field and remote data acquisition, consequence modeling of both the pipeline and facility hazards and an assessment of risk levels associated with the interactive risk synergy. |
||||
| P2001 |
ESCAPE, EVACUATION AND RESCUE RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT PROJECT
- Phase 1 CLIENT: Transportation Development Centre DATE: 2000-2001 DESCRIPTION: A major multi-disciplinary project on the development of appropriate escape, evacuation, and rescue (EER) systems for east coast bottom founded and floating installations associated with the oil and gas industry off the East Coast of Canada. The work consists of a worldwide literature search, followed by the development of a risk profile tool, an expected value and a Monte Carlo simulator, of each component of and the entire EER process and the integrated process. Consideration of equipment reliability and human factors in the face of accident effects, emergency panic conditions, and the entire spectrum of weather conditions is incorporated. Conclusions will be generated on optimal systems as well as further research priorities for both the development of appraisal methods, technologies, and a regulatory framework for EER provisions in the study area. EER R&D projects Phases I, II, and III-B are described under project numbers: P2101, P2201, P2301, P2401, and P2501. More information can also be found on our PBS downloads page. |
||||
| 1999 | |||||
| P9918 |
EL BIBAN POWER PLANT AND SYSTEMS
RELIABILITY AND MAINTAINABILITY ANALYSIS
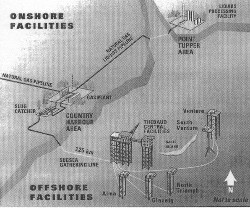
CLIENT: Centurion International Inc. DATE: 1999 - 2000 DESCRIPTION: The El Biban Power Plant and associated equipment for the SEEB Electrical Company in Tunisia, Africa is proposing the development of a power plant and associated power distribution system fueled by an offshore oil field located in the southern Mediterranean Sea just off the coast of Tunisia. The system is a complex consisting of the wellhead platform, subsea pipeline, onshore battery and separation equipment, various interconnecting pipelines, the main power plant and turbine generator, a high-voltage power line to the STEG Substation and various supporting facilities. An integrated downtime risk assessment including both short-duration expected downtime for maintenance and temporary repairs and potential catastrophic or major failure downtime risk was assessed. The work was conducted through the utilization of industry and proprietary data bases for equipment failure rates, interruption times, times to repair, environmental data, and general reliability assessment combined through a probabilistic model capable of generating expected values and their distributions through a Monte Carlo procedure. Click on the thumbnails to view enlarged image.
|
||||
| P9918 |
EL BIBAN POWER PLANT AND SYSTEMS
RELIABILITY AND MAINTAINABILITY ANALYSIS
CLIENT: Centurion International Inc. DATE: 1999 - 2000 DESCRIPTION: The El Biban Power Plant and associated equipment for the SEEB Electrical Company in Tunisia, Africa is proposing the development of a power plant and associated power distribution system fueled by an offshore oil field located in the southern Mediterranean Sea just off the coast of Tunisia. The system is a complex consisting of the wellhead platform, subsea pipeline, onshore battery and separation equipment, various interconnecting pipelines, the main power plant and turbine generator, a high-voltage power line to the STEG Substation and various supporting facilities. An integrated downtime risk assessment including both short-duration expected downtime for maintenance and temporary repairs and potential catastrophic or major failure downtime risk was assessed. The work was conducted through the utilization of industry and proprietary data bases for equipment failure rates, interruption times, times to repair, environmental data, and general reliability assessment combined through a probabilistic model capable of generating expected values and their distributions through a Monte Carlo procedure. |
||||
| P9917 |
ASSESSMENT OF REPORT ON RELATIVE CRITICAL SOUR GAS WELL
RISK ASSOCIATED WITH DIFFERENT DRILLING TECHNIQUES
CLIENT: Energy and Utilities Board DATE: 1999 - 2000 DESCRIPTION: The work involved the detailed review of an assessment of the relative risks associated with the drilling of critical sour gas wells based on overbalanced jointed pipe drilling and underbalanced jointed pipe or coiled tubing drilling. |
||||
| P9914 |
ASSESSMENT OF RISKS AT ROAD-RAILWAY CROSSINGS
CLIENT: Code Hunter and Associates DATE: 1999 DESCRIPTION: The work consisted of the generation of definitive risk measures associated with a variety of road-railway level crossings including passive crossings, flashing light and bell crossings, and gated crossings. The work was based on nation wide statistics collected from the Transportation Safety Board, as well as industry confidential statistics provided by the transportation companies. Results of the work were utilized in support of a litigation associated with a major railway crossing accident. |
||||
|
P9709 .44 |
GOLDBORO GAS PLANT COMPRESSION HAZOP
CLIENT: Sable Offshore Energy Project DATE: 1999 DESCRIPTION: Following the detection of a design fault, a full HAZOP of the compression facilities was undertaken, facilitated by Bercha with an SOEP expert team. Due to the complex nature of the system, the high level of expertise of the team, and the shortage of time, the initial mode was addressed using a full guide word HAZOP, but the balance of the nodes and operating modes were optimally accomplished using a knowledge-based HAZID approach. Important technical recommendations significantly improving system reliability were generated from the work. |
||||
|
.43 |
PLATFORM FIREWATER SYSTEM HAZOP
Click on the thumbnails to view enlarged image.
|
||||
|
P9709 .42 |
FRACTIONATION PLANT HAZID & CE
CLIENT: Sable Offshore Energy Project DATE: 1999 DESCRIPTION: A precommissioning and commissioning procedure HAZID and Critical Examination of the procedure was conducted including facilitation of the HAZID with an expert team, scribing of results utilizing proprietary software, and the publication of a comprehensive final report describing the results and recommendations from the work. |
||||
| P9909 |
BRISK
SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT
CLIENT: National Research Council DATE: 1999 DESCRIPTION: The work included the development of specialized linear and point source risk analysis software for application to quantitative risk assessments associated with linear facilities such as pipelines and highways and point sources such as gas processing facilities, wellheads, and refineries. More information on BRISK. |
||||
| P9907 |
CHEVRON GAVIOTA OIL AND GAS PROCESSING FACILITY –
CONDITION R1 REVIEW PROCESS CLIENT: County of Santa Barbara Energy Division DATE: 1999 DESCRIPTION: A semi-qualitative risk assessment of the risks mitigation provisions and conditions associated with a variety (over 12) scenarios for the future of the Chevron Gaviota oil and gas processing facility. |
||||
| P9906 |
PRODUCTION WELL SSSV RISK ASSESSMENT
|
||||
| P9905 |
REVIEW OF INCIDENT REPORTS ASSOCIATED WITH WILD ROSE PIPE
CORRIDOR CLIENT: Kiewit Industrial Canada Ltd. DATE: 1999 DESCRIPTION: A qualitative assessment within the context of the Suncor rating system was conducted to provide perspective based on fundamental risk assessment principles on a variety of incidents associated with activities of Kiewit on the Suncor construction site. |
||||
|
P9902 .2 |
HERMOSA BEACH QUANTITATIVE RISK ASSESSMENT
CLIENT: City of Hermosa Beach DATE: 1999 DESCRIPTION: Risk analysis and engineering consulting services were provided to the City of Hermosa Beach to assess, recommend mitigation, and quantify and define risks associated with the proposed MacPherson Oil project in the City of Hermosa Beach. |
||||
|
P9709 .42 |
FRACTIONATION PLANT HAZID & CE
CLIENT: Sable Offshore Energy Project DATE: 1999 DESCRIPTION: A precommissioning and commissioning procedure HAZID and Critical Examination of the procedure was conducted including facilitation of the HAZID with an expert team, scribing of results utilizing proprietary software, and the publication of a comprehensive final report describing the results and recommendations from the work. |
||||
|
P9709 .41 |
ONSHORE 26” GAS AND NGL PIPELINE HAZOP
CLIENT: Sable Offshore Energy Project DATE: 1999 DESCRIPTION: A detailed HAZOP for the NGL pipeline was facilitated, scribed, and reported by Bercha together with the HAZOP sessions conducted together with a team of experts from SOEP and owner companies. |
||||
|
P9709 .40 |
ENGINEERING CHANGE NOTICE (ECN) HAZOP
CLIENT: Sable Offshore Energy Project DATE: 1999 DESCRIPTION: A high-level knowledge based HAZOP procedure was facilitated, scribed, and reported by Bercha to ascertain that document and action integrity be maintained for the Engineering Change Notices generated and associated follow up procedures. |
||||
|
P9709 .39 |
NORTH TRIUMPH HAZID/CE CLIENT: Sable Offshore Energy Project DATE: 1999 DESCRIPTION: A precommissioning and commissioning procedure HAZID and Critical Examination of the procedure was conducted including facilitation of the HAZID with an expert team, scribing of results utilizing proprietary software, and the publication of a comprehensive final report describing the results and recommendations from the work. |
||||
|
P9709 .38 |
GOLDBORO GAS PLANT HAZID/CE
CLIENT: Sable Offshore Energy Project DATE: 1999 DESCRIPTION: A precommissioning and commissioning procedure HAZID and Critical Examination of the procedure was conducted including facilitation of the HAZID with an expert team, scribing of results utilizing proprietary software, and the publication of a comprehensive final report describing the results and recommendations from the work. |
||||
|
P9709 .37 |
STRAIT OF CANSO PIPELINE CROSSING RISK ASSESSMENT
CLIENT: Sable Offshore Energy Project DATE: 1999 DESCRIPTION: A risk assessment associated with two principal types of crossing installations for the common trench pipelines across the Strait of Canso were investigated. The first installation involved a combination of bottom-lay, trenching, and successive layer armoring. The second alternative involved directional drilling. The risk assessment considered both risks associated with the construction and installation process as well as operational risks. Both risks directly attributable to the crossing installation and its operation and intrinsic risks (such as internal corrosion) independent of the installation method were assessed and quantified. Conclusions and recommendations were made. |
||||
| 1998 | |||||
| P9809 |
TRANSGAS CONSEQUENCE ANALYSIS – REGINA
AREA NATURAL GAS PIPELINES CLIENT: TransGas DATE: 1998 DESCRIPTION A consequence assessment for a designated set of segments of the TransGas pipeline network in the vicinity of the City of Regina was carried out. The principal technical steps of the consequence assessment included hazard scenario definition and quantitative characterization. Consequence evolution and consequence modeling, consequence potential assessment and detailed consequence analysis. A total of 11 segments was studies in detail including the above steps, while a detailed consequence assessment giving estimates of both casualties and property damage based on a worst-case situation was also conducted. Conclusions and recommendations were presented. |
||||
| P9808 |
RISK FROM MAGNETIC LEVITATION TRAINS TO ADJACENT BURIED
STEEL PIPELINES CLIENT: Donahue and Company Inc., U.S.A. DATE: 1998 DESCRIPTION: High-level consulting work directed at defining the risks associated with the operation of Mag-Lev trains parallel to pipelines. Specifically, effects of the electromagnetic pulsations associated with the train operation on induced currents in the steel pipeline were considered together with mitigation measures. Following a literature survey of current magnetic levitation (Mag-Lev) train systems approaching the operational stage, a preliminary assessment of risks associated with the operation of Mag-Lev trains had a potential to induce substantial currents in adjoining steel pipelines and mitigation measures would have to be taken in order to avoid significant pipeline damage. |
||||
| P9804 |
HERMOSA BEACH PROJECT INTEGRATED RISK ASSESSMENT
CLIENT: City of Hermosa Beach, CA, USA DATE: 1998 DESCRIPTION: Integrated assessment of the proposed MacPherson Project to be located in a medium density residential and commercial area in Hermosa Beach was conducted. The work consisted of site visits, review of existing reports and data, a detailed QRA, attendance at stakeholders meetings, and attendance at public council meetings. The integrated risk assessment was carreid out in considerable detail to consider both non-homongenous population densities in space and time, and a variety of weather conditions in order to assess both representative and worst-case situations. Integrated risk measures, including individual risk, risk matrices, and risk spectra were generated in support of the work and presented at the city’s Council meeting September 1998. |
||||
| P9803 |
ENGINEERING FEASIBILITY STUDIES FOR HYDROCARBON PRODUCTS
PIPELINE EASEMENTS CLIENT: Brown, Winfield, and Cansoneri, Union Pacific Railway DATE: 1998 DESCRIPTION: Assessment of the value of pipeline easements on Union Pacific Railroad right-of-ways was conducted with special emphasis on construction, engineering, and risk issues. Constructibility of pipelines in the vicinity of the existing pipelines was quantitatively assessed. Engineering issues involving the operability and design requirements of pipelines operated in close proximity ranging from common trench installations to separations in excess of 20’ were considered and quantitatively and qualitatively described to support the pipeline easement value assessment. |
||||
|
P9709 .33 |
SABLE OFFSHORE ENERGY PROJECT HAZOP FACILITATION
CLIENT: Sable Offshore Energy Project DATE: 1998 DESCRIPTION: A series of HAZOP sessions was facilitiated by the Bercha Group including organization of HAZOP team, facilitation of HAZOP services, and HAZOP reporting. Specifically, HAZOP was carried out for the specific onshore facilities including the gas processing facility at Goldboro and the NGL fractionation plant at Point Tupper. |
||||
| 1997 | |||||
| P9709 |
SAFETY CASE FOR THE SABLE OFFSHORE
ENERGY PROJECT CLIENT: Sable Offshore Energy Project DATE: 1997 - 2001 DESCRIPTION: The Bercha Group was the prime contractor for the Concept Safety Evaluation of the Sable Offshore Energy Project, providing overall project management, conducting the CSE for all onshore facilities, as well as selected segments of the offshore facilities including the Straits of Canso crossing and ship/collision probability assessments associated with the offshore platforms. Bercha conducted the onshore analysis through a systematic sequence of data assimilation, hazard scenario development, frequency evaluation, consequence assessment, risk analysis, risk acceptability evaluation, risk mitigation measure development, and resultant or residual risk assessment. For each of the principal facility components, including marine pipeline, gas processing plant, NGL Pipeline, NGL Fractionation Plant, and NGL Products Distribution Terminal. Subsequent QRAs relating to the project were conducted by Bercha in the area of Statia Marine Terminal risk assessment, fire and explosion consequence analysis, offshore escape evacuation and rescue studies, and general risk management and safety program development for the safety case associated with the project. |
||||
| P9704 |
ECONOMIC RISK ANALYSIS OF SCHEDULE IMPLICATIONS FOR THE
ALPINE DEVELOPMENT PROJECT CLIENT: Tri-Ocean Engineering DATE: 1997 DESCRIPTION: A Monte Carlo simulation of the project time flow, together with the principal uncertainties associated with a schedule 1 analysis for a development project on the Alaskan North Slope was carried out. Principal areas of uncertainty included those associated with labour requirements and rates on the North Slope, success of the marine transport of principal equipment items around Point Barrow (given a 3 to 6 week ice-free window), logistics and operations on the tundra given a variability of weather windows for their conduct, and the integration of all these activities into a total project schedule risk evaluation. |
||||
| 1996 | |||||
| P9657 |
DEVELOPMENT OF COMMERCIAL HYDROCARBON EXPLORATION OPPORTUNITIES
IN MALAYSIA CLIENT: CS Resources Limited DATE: 1996 DESCRIPTION: A high level program for the identification and development of commercial opportunities for the special capabilities of CS Resources International within the Malaysian jurisdiction. The work involved the gathering of reserve, development, and production data for the Malaya, Baram Delta, and Sabah Basins and the analysis of selected clusters of fields within the context of certain operational and economical parameters capable of being optimally met by the client company. Work included the design of a detailed presentation for international audiences showing the highlights of the Malaysian Development program envisioned. |
||||
| P9655 |
ANALYSIS OF RISKS ASSOCIATED WITH OIL
PRODUCTS PIPELINE ON RAIL ROAD RIGHT OF
WAY CLIENT: Southern Pacific Transportation Company, California & Delaware, U.S.A. DATE: 1996 DESCRIPTION: The provision of expert consultant services in the area of pipeline engineering, right of way management, and easement evaluation related to the operation of an existing oil product pipeline located on a rail road right of way within the city of Los Angeles. |
||||
| P9653 |
ESTABLISHMENT OF PUBLIC SAFETY RISK THRESHOLDS FOR LAND
USE PLANNING PURPOSES CLIENT: County of Santa Barbara, California, U.S.A. DATE: 1996 DESCRIPTION: Work is part of an ongoing program directed at the enhancement of safety through the incorporation of risk based guidelines in land use planning regulations. The work included the development of an objected method for assessing societal risk in the vicinity of hazardous facilities. The method developed was based on casualty and fatality risk spectra and included the development of a detailed procedure for implementing the guidelines. Technical review, sample calculations, and attendance at information sessions and hearings constituted the work. |
||||
| P9650 |
RISK IMPLICATIONS OF HIGH POWER TRANSMISSION LINES IN
PROXIMITY OF PETROLEUM PIPELINES OF
RAIL ROAD RIGHT OF WAYS CLIENT: Southern Pacific Transportation Company, California, U.S.A. DATE: 1996 DESCRIPTION: Vision of expert consulting services and development of expert testimony relating to the risks and costs associated with the operation of electrical transmission lines on a rail road right of way within limits of the city of Los Angeles. |
||||
| P9603 |
INSTITUTION OF TEST METHODS FOR ICE RUBBLE CLIENT: K.R. Croasdale and Associates Limited DATE: 1996 DESCRIPTION: The Development of a detailed program for the evaluation of global crushing strength of ice rubble formations including rubble piles, unconsolidated, semi consolidated, and consolidated ridges, and pile ups in the vicinity of offshore structures. Methods included the design of test procedures for the evaluation of pressure and global forces utilizing existing test facilities at the institute of ice dynamics and in private laboratories. |
||||
| 1995 | |||||
| P9524 |
CONSTRUCTION ENGINEERING FOR HIGH PRESSURE GAS PIPELINE
CLIENT: Hill, Farrrer, and Burill DATE: 1995 DESCRIPTION: Analysis of effects of high pressure gas pipeline in vicinity of commuter train track, including evaluation of interaction of pipeline and railway in a track twinning scenario. Work was conducted through Hill and Company on behalf of the Orange County Transportation Association, for a location in Orange County, California, near Newport Beach. |
||||
|
P9513 .2 |
RISK ANALYSIS OF EXISTING SANTA FE PIPELINE WITHIN
SOUTHERN PACIFIC TRANSPORTATION
COMPANY EASEMENT CLIENT: Brobeck, Phleger & Harrison DATE: 1995 DESCRIPTION: An analysis of the risks to public and worker safety associated with the operation of a high pressure gasoline pipeline located in the Southern Pacific Right-of-way, extending from California to El Paso, Texas, was conducted. Particular consideration was given to the distinctive effects on risk of the location of the pipeline within the Right-of-way in close proximity to a frequently used freight and passenger train railway track. Risk indices were computed for urban and rural conditions, and an integrated risk for the pipeline operation was assessed based on actual conditions along the Right-of-way. The work served as support for expert testimony by Dr. F.G. Bercha in litigation between Southern Pacific Transportation Company and Santa Fe Pipeline Company, in support of Southern Pacific's position. |
||||
|
.1 |
PIPELINE AND FIBRE OPTIC CABLE ENGINEERING, CONSTRUCTABILITY
AND RISK ANALYSIS CLIENT: Brobeck, Phleger, and Harrison DATE: 1993 - present DESCRIPTION: The project consisted of the preparation and presentation of expert testimony on the general problem of construction of new pipeline or fibre optic cable facilities in the vicinity of an existing high pressure oil products line located on a railway right-of-way. Studies consisted of the development of construction scenarios for locations at different separation distances from the pipeline and associated cost and risk evaluations. Unit costs were developed for the construction of new pipeline facilities at spacings ranging from approximately 1 foot tangent to tangent, to 10 feet and more from the existing pipeline. Worker and public safety risks associated with the close proximity construction scenarios were also conducted, based on construction in urban and rural conditions surrounding the right-of-way. In addition the engineering model of a possible equivalent pipeline system form California to Texas was developed and a replication cost estimate was generated. The work consisted of analysis computer modelling, engineering calculations, site visits at facilities locations in California (Richmond, Benicia, Martinez Merced), cost estimating reporting, depositions, and presentation of export testimony. |
||||
| P9510 |
JOINT INDUSTRY PROJECT ON RIDGE AND RUBBLE LOADS CLIENT: K. R. CROASDALE AND ASSOCIATES DATE: 1995-96 DESCRIPTION: A joint-government industry project to develop new models for the prediction of ridge and rubble loads on fixed offshore structures. The project has included two sets of ice tank experiments of ridges being indented by structures, the development of an in-situ test method for the strength of rubble, and the detailed investigation of two new methods for the determination of ridge load, which both involve the full time analysis of the indentation of the ridge. The project is also examining the assumption of Mohr-Coulomb behavior of the ice rubble, the separation of the strength into components of cohesion and friction, and the physical characteristics of the ice motion against and around the structure. |
||||
| P9509 |
QUANTITATIVE RISK ANALYSIS OF A PROPOSED COAL HANDLING AND
STOCKPILE STORAGE OPERATION AT
TANJUNG MANIS FOR INCLUSION IN AN ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT
ASSESSMENT CLIENT: U.P. Environmental Services Sdn. Bhd., Kuching, Sarawak, Malaysia DATE: 1995 DESCRIPTION: An integrated public safety, worker safety, and environmental risk analysis was conducted for the proposed coal handling and storage operation located on the Batangiajanj River at Tanjung Manis in Northern Sarawak, Malaysia. The principal acute risks studies were those associated with the stockpile spontaneous combustion and potential dust explosions contained in a sea-going freighter hold during coal unloading. The work consisted of the assessment of initiating event frequencies, potential consequence analysis, and recommendation of risk mitigation measures. |
||||
| P9504 |
ICE LOAD CONCENSUS CLIENT: K. R. CROASDALE AND ASSOCIATES DATE: 1995-96 DESCRIPTION: A joint-government industry project to achieve consensus on ice load levels for a number of typical ice load events. Thirteen groups were asked to predict the load for five individual load cases, for a single event occurrence, and for the 1% exceedance load. Bercha have been involved in the analysis of the predictions including comparisons between the predicted loads, the methods used, the databases used, and the estimates of the effects of dynamics, and the 1% exceedance loads. A workshop between the participants and the predictors will be held to possibly arrive at some consensus regarding the methods to be used, the interpretation of databases, and hence arrive at some narrowing of the range of predictions. |
||||
| 1994 | |||||
| P9428 |
PA9428 NON-LINEAR FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS 42" PIPE TEES
CLIENT: FOOTHILLS PIPE LINES LTD DATE: 1994-95 DESCRIPTION: Elastic-Plastic analyses of two 42" pipe tees in a metering station were analysed for changes in the operating conditions of the natural gas pipeline, of which they formed part. Preliminary pipe stress analyses had suggested that these tees were over-stressed under certain conditions, but the margin was sufficiently narrow to warrant more detailed analysis of the tees. Finite element models of the pipe tees were developed using the commercial finite element package, Ansys. Models were developed using two forms of three-dimensional solid iso-parametric elements, and iso-parametric shell elements. Analyses were carried out for the previous operating conditions, and the proposed new operating conditions. The non-linear behaviour used was for material non-linearity only, using a von Mises yield criterion for the steel in the pipes. The results were input into a fatigue calculation using some estimated load cycles for the extreme load conditions. It was found that, on a single load cycle, some non-linearity did occur in the crotch of the tee, but that it was of very limited extent, Strain hardening was sufficient to limit stresses in subsequent cycles to the elastic range. It was concluded that the overall reliability of the pipe Tees was not compromised by the revised operating conditions. |
||||
|
P9426 |
NON-LINEAR FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF ICE RIDGE KEEL
BEHAVIOUR CLIENT: PUBLIC WORKS CANADA DATE: 1994-95 DESCRIPTION: Non-linear finite element analyses of the interaction between the rubble in an ice ridge keel and a cylindrical structure were undertaken. Analyses were carried out in both two- and three-dimensions. The rubble was modelled as a Mohr- Coulomb material with and without dilatancy. The structure was modelled as a rigid body, and the interface as either having, or not having, friction. The analysis was carried out assuming that there existed a continuous solid ice layer on the surface. Two forms of analysis were carried out: one in which the ice layer was made to fail against a sloping structure, and the other, in three dimensions, in which the ice layer was assumed to remain intact, but in which the ice rubble could slide along the underside of the ice layer. The rubble's natural buoyancy was modelled by appropriate mass density and accelerations. Each analysis was carried out by stepping the far-field of the ridge towards the structure in preset displacement steps, which the program automatically reduced as required to achieve equilibrium and convergence of the solution. Considerable difficulties were encountered with the curved interface between the rubble and the cylindrical structure, and particularly where the rubble left the structure at the back. Very large strains caused the interface nodes to oscillate between target elements, causing convergence problems. For extreme ridges (20 meters deep) maximum loads of the order of 17 MN were obtained. |
||||
|
P9408 P9418 |
DYNAMIC ANALYSIS AND MODIFICATION OF PUMP MOTOR BASE CLIENT: FEDERATED PIPELINES LIMITED DATE: 1994 DESCRIPTION: A pump used in an oil pipeline, was experiencing unacceptable vibrations at speeds within its normal operating speed range. Field analysis of the pump and pump base had concluded that the steel base which supported the pump motor may have been causing the vibrations. A detailed dynamic finite element analysis of the pump base was undertaken to establish the frequencies and mode shapes of the fundamental vibration mode of the base. Although there were modes which would have caused the forms of deformation being observed in the rotor, the frequencies of these nodes were higher than the observed frequencies by an order of magnitude. Structural reinforcement of the base was designed to limit the amplitudes of these vibrations. It was finally concluded that the vibrations were being caused by the rotor itself. |
||||
|
P9315 |
NORTHUMBERLAND STRAIT CROSSING ICE ENGINEERING Click on any of the thumbnails for an enlarged view. |
||||
| 9403 |
BRICK DURABILITY ALGORITHM CLIENT: PUBLIC WORKS CANADA DATE: 1994 DESCRIPTION: A computer algorithm developed to assess the reliability of brickwork in buildings was tested. The algorithm required a considerable amount of environmental data for typical urban locations in Canada, and the merging of this data to obtain frequencies of specific combinations of environmental conditions. Once the data base had been obtained and analysed, the algorithm was tested for a number of typical locations to derive the frequency of failure as defined by spalling of the brickwork. |
||||
| 1993 | |||||
|
P9324 |
SPECIFICATION OF STRUCTURAL CHARACTERISTICS OF MOBILE ARCTIC
CAISSON, MOLIKPAQ CLIENT: B. WRIGHT AND ASSOCIATES DATE: 1993-94 DESCRIPTION: A 1/30 scale model of the Molikpaq was to be developed at the National Research Council of Canada ice tank in Ottawa. In order to construct the model and to provide the appropriate instrumentation to permit comparisons between the ice tank results, and the full scale data acquired during the structure's deployments in the Beaufort Sea, NRCC contracted to have the necessary structural characteristics provided. As Bercha had a long history of developing analytical models of the Molikpaq, they were asked to provide this information. The information included the overall stiffness of the structural system as it was deployed at Amauligak I-65, the relative stiffnesses of the individual structural components, and the primary load paths, the mass distribution for the same deployment, and the dynamic characteristics of the system. The specification of the dynamic characteristics included the natural frequencies of the complete system, and major components, and the level of damping of the various components. This latter parameter included the estimation of damping with and without the presence of ice. |
||||
|
P9321 |
FINITE
ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF REINFORCED CONCRETE STACK CLIENT: MONENCO DATE: 1993 DESCRIPTION: TransAlta Utilities, the owner and operator of the Wabamun electrical generating plant, and the Alberta Department of the Environment, wished to create additional access holes in the largest of reinforced concrete stacks in order to permit sampling of exhaust gases. Prior to the creation of the holes, they wished confirmation that the holes would not critically alter the integrity of the stacks. To do this, a non-linear finite element analysis of a portion of the concrete stack was carried out under the effects of extreme operating conditions, and the design wind pressures. Analyses were carried out both for the current arrangement of holes and with the proposed additional holes. The analysis was carried out with a special purpose non-linear finite element program which accounted for the tension-weak characteristics of concrete, the presence of reinforcing steel, and the time dependent behavior of concrete. The results indicated that the proposed additional holes did not compromise the reliability of the stack. |
||||
|
P9310 .01 |
ICE LOAD
SENSITIVITY FOR EAST COAST STRUCTURES CLIENT: NATIONAL ENERGY BOARD DATE: 1993 DESCRIPTION: Sensitivity of specified environmental ice design loads in accordance with CSA S471. Carried out simulations of ice forces from impacts by: icebergs, bergy-bits, and sea ice with fixed and floating production structures in the Hibernia area of the Grand Banks. The analyses incorporated energy decay algorithms for the impact analysis with appropriate energy sinks depending on the particular interaction. For fixed structures these included crushing of ice as well as elastic structure response, and iceberg rotation and translation. For floating structures, local elastic and permanent deformation of the structure was included. Data on iceberg frequencies, dimensions, shape, and velocities were obtained from various sources to provide the most reliable distributions. For bergy-bits, recent reported data by Crocker was used for the size distribution. Sensitivities were carried out on ice strength, iceberg velocity, and iceberg arrival rate. Of these, the first was found to have the most effect on the specified design forces, while the second, velocity, was found to have the least effect. |
||||
|
P9303 .01 |
RISK BASED SITING AND PERMITTING OF HAZARDOUS ENERGY
RELATED FACILITIES CLIENT: County of Santa Barbara, California Utilities Commission DATE: 1993-1994 DESCRIPTION: The objective of this study was to develop the basis for a policy on application of risk analysis in the siting and permitting of hazardous energy related facilities in the County of Santa Barbara. General classes of facilities considered explicitly were oil and gas, automotive fuel, and electrical facilities. Only acute or immediate risks as opposed to chronic or long term risks were included in the scope of work. Fundamentals of risk analysis were reviewed to establish a basis and terminology for the balance of the work. The general procedures for implementing risk considerations in the planning process were then described. Results from a review of the general types of hazardous energy related facilities which exist or may exist in the near future in the County of Santa Barbara included: a) classification of the facilities into oil and gas, automotive fuel, and electrical categories and sub-categories such as gasoline, compressed natural gas, methanol, and ethanol stations in the automotive fuel category. b) a brief description of the relative hazardousness of the principal substances handled by the facilities. c) a general description and summary of the hazards associated with each type of facility. d) a review of both US and worldwide guidelines and regulations designed to manage acute risks to the public. e) a discussion of the role of risk analysis in the context of the planning processes for the County of Santa Barbara. f) specific recommendations for the implementation of the results from this work. |
||||
| P9301 |
DEVELOPMENT OF RISK MANAGEMENT PROGRAM FOR THE
ENGINEERING, CONSTRUCTION, AND
OPERATION OF HIGH PRESSURE SOUR GAS LINE CLIENT: Shell Canada Limited DATE: 1993 DESCRIPTION: A risk management program was developed for the operation of a high-pressure sour gas pipeline from a gathering system to a sour gas treatment plant. All potential pipeline system failure scenarios such as thermal stress, differential settlement, third party effects, and other scenarios identified in previous studies by the Bercha Group were considered in this program. These scenarios were prioritized through the assignment of risk indices, considering probability and consequence severity, and a series of mitigative measures were developed and evaluated quantitatively. A specific risk management plan detailing the mitigative measures, technical responsibilities, and implementation procedures was then developed to address each principal risk scenario. Bercha risk analysts and engineers advised the Shell project and operating personnel in conjunction with the Shell engineering partner responsible for design and construction. |
||||
| 1992 | |||||
|
P9231 .01 |
INVESTIGATION OF ICE GROWTH AND DECAY SCHEMES FOR REGIONAL ICE
CLIENT: ICE CENTRE - ENVIRONMENT CANADA DATE: 1992-3 DESCRIPTION: Scientific assessment of existing ice growth and decay models for possible incorporation in the Multi-Category Regional Ice Model (MCRIM). A team of experts was assembled to review possible approaches and recommend models which could be included in MCRIM without altering the basic dynamic formulation and which would permit MCRIM to execute in an operational mode. The experts recommended a two-part approach: the Semtner zero-layer model for basic ice cover and a wave-driven model for edge effects. Algorithms were developed and coded into MCRIM as new subroutines which could be executed as options. All of the new coding was fully documented. A comprehensive series of sensitivity analyses were carried out to illustrate the effect of the new modelling on ice growth and decay at the top and bottom surfaces of the ice/snow slab. The necessary additional data to permit MCRIM to run with the new algorithms was obtained. Further, new data for the verification periods (see PA 9114) was also obtained. The verification procedures for the two periods for the east coast were run in a series of analyses to illustrate the effect of the new algorithms on ice edge movement and ice concentrations. |
||||
|
P9231 .02 |
REGIONAL
ICE MODEL THERMODYNAMICS CLIENT: ATMOSPHERIC ENVIRONMENT SERVICES, ICE CENTREDATE: 1992 DESCRIPTION: The study consisted of a review of existing forms of the regional ice model utilized for the prediction of short and long term ice motion and ice climatology, followed by the development of specific algorithms for improving modelling accuracy and efficiency. Model performance was evaluated through comparison to a series of real time ice observations obtained from airborne radar and satellite data. |
||||
| P9228 |
COMMISSIONING AND START UP OF OPERATIONS
READINESS REVIEW FOR A WORLD SCALE
SOUR GAS PRODUCTION SYSTEM AND TREATMENT PLANT CLIENT: Shell Canada Limited DATE: 1992 DESCRIPTION: An operational readiness review was carried out on a world scale sour gas production and treatment facility at Caroline to identify any critical deficiencies or concerns in the commissioning and start up plans. The review team included risk consultants in addition to independent operating personnel with instrumentation, operations, and maintenance experience. A broad cross section of the facilities operating team, including contractors, was interviewed to identify significant concerns, which may delay or endanger a smooth start up. The review was restricted to commissioning and start up and did not address steady state operations nor did it involve a detailed inspection of equipment. The review did provide an assessment of the management systems and implementation program performance. Results from the operational readiness review included identification of the principal concerns among the following categories: a) Organization, b) Safety Procedures, c) Equipment Readiness, d) Training, and e) Emergency Response. Following the identification of concerns, conclusions were presented which prioritized the concerns so they could be effectively addressed. In addition, any exceptional aspects of the commissioning and start up plans as presently being implemented were highlighted. |
||||
|
P9219 |
RESEARCH
AND DEVELOPMENT OF FINITE ELEMENT SOFTWARE CLIENT: NATIONAL RESEARCH COUNCIL OF CANADA DATE: 1992 DESCRIPTION: A series of Finite Element Software programs which were originally developed as research tools were modified and augmented to allow their execution on IBM PC compatible computers. These improvements included, in some cases, whole-scale modifications to the original code to eliminate dated Fortran usage and introduce memory management processes prevalent in desktop PC's. Other improvements included the introduction of pre- and post-processors which simplified the preparation of data input, and the interpretation of output results. These were set up to run under a Windows environment. Finally, the ability to output results graphically was also added to the programs. This latter improvement required the creation of complex data management routines to permit user control of the results being output, and the orientation and scale of the plot. |
||||
| P9213 |
LEAK HAZARD ANALYSIS OF A HIGHER PRESSURE NATURAL GAS
PIPELINE CLIENT: Westcoast Energy Inc. DATE: 1992 DESCRIPTION: During construction of the new natural gas pipeline from the mainland to Vancouver Island, British Columbia, there was concern regarding potential hazards from an industrial facility located near the pipeline right of way. A study was therefore carried out to estimate the hazards resulting from any leak from the pipeline. Safety and property hazard zones, as defined by delayed or immediate ignition of potential leaks, were estimated using consequence models. Plume dispersion calculations were performed using the GASCON 2 model, while the effects on people from a fire were estimated based on the approach developed by Considine and Grint and using the probit equation of Eisenberg. The effects of thermal radiation on surrounding property were also evaluated using empirical data. |
||||
| P9212 |
PROBABILISTIC ANALYSIS OF RESIDENTIAL AND INDUSTRIAL
DEMAND FOR NATURAL GAS FROM A
REGIONAL DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM CLIENT: Northwestern Utilities Limited DATE: 1992 DESCRIPTION: The client contracts for natural gas supply from a variety of producers, then provides an integrated delivery system of natural gas to many communities in the north central region of the province of Alberta. The majority of natural gas is supplied on an as and when required basis, however a number of large industrial users contract to specific delivery amounts. In order to design the gas delivery system including capacity requirements for underground storage, the client must estimate the maximum total gas demand, which consists of both temperature dependent and temperature independent components. Current designs were developed from worst case scenarios and the objective of the present study was to convert such criteria to a probabilistic basis more representative of the factors affecting the delivery system. An in-depth probabilistic analysis was therefore carried out on the extensive environmental data bases and gas consumption records for the client delivery system. The detailed design criteria for both the temperature dependent and temperature independent components of the gas load were evaluated and compared to the total gas load on the system. |
||||
|
P9208 |
SIMULATION
AND MODELING SERVICES FOR NORTHUMBERLAND STRAIT PROJECT
DATE: 1992-3 |
||||
| P9206 |
COMPARISON OF RISKS BETWEEN ALTERNATIVE RAIL AND TRUCK
MODES FOR TRANSPORTING LPGs CLIENT: Shell Canada Limited DATE: 1992 DESCRIPTION: An investigation was carried out on the risk impacts from changing the mode of liquid petroleum gas (LPG) transportation in Eastern Canada from a rail operation to a truck operation. Of particular interest was the potential relative change in risk exposure corresponding to a change in transportation mode. The work was commissioned in phases, beginning with a top level analysis for management and continuing with a more detailed analysis providing a site and operation specific comparison. The preliminary risk analysis provided a management overview of historical rail and truck accident and release frequencies, in addition to the distribution of consequence hazard zones associated with an LPG release. Frequency analyses for both modes of transportation were based on analyses of published generic data for the transportation industry in Canada and North America. The consequence analysis involved both a statistical analysis of historical accident consequences and modeling of potential spill consequences in order to determine the associated hazard distances. The second phase of work continued with a more detailed analysis of site specific accident data and public exposure data. |
||||
|
P9205 |
FINITE
ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF REINFORCED CONCRETE STACK
DATE: 1992 |
||||
| 1991 | |||||
| P9119 |
PRE-COMMISSIONING OPERATIONS AUDIT AND OFFSITE PRELIMINARY
RISK ASSESSMENT FOR A LARGE-SCALE
CRUDE OIL UPGRADING FACILITY CLIENT: Husky Oil Bi-Provincial Upgrader, Saskatchewan DATE: 1992 DESCRIPTION: Husky Oil Operations Ltd. as Project Manager of the Joint Venture partners including Husky Oil, the Canadian Alberta and Saskatchewan Governments, and HRI constructed the Bi-Provincial Upgrader (BPU) to produce synthetic crude and asphalt from a 65%/35% volumetric blend of Lloydminster and Cold Lake heavy oils, respectively. The study was carried out as part of the Pre-Commissioning activities for the BPU and included an operational audit and an offsite risk assessment. A Pre-Commissioning Audit of the BPU was carried out to ensure operational readiness for commissioning and operating the facilities through the identification of critical deficiencies or concerns in the start-up plans. An independent audit team interviewed a broad cross-section of the BPU staff in order to identify problem areas, potential difficulties, or concerns, which had the potential to delay or endanger a smooth start-up of the facilities. Results included a list of prioritized concerns in the areas of organization, procedures/safety, equipment readiness, training, emergency response and unit specific concerns. These results provided a basis for pro-active measures to increase the potential for a successful start-up of a very large and complex process facility. |
||||
| P9117 |
DEVELOPMENT OF A POLICY PAPER ON GAS
PIPELINE SAFETY CLIENT: County of Santa Barbara, California Gas Commission DATE: 1991 DESCRIPTION: The County of Santa Barbara commissioned the development of a policy paper as part of its continuing efforts as a regulatory agency overseeing gas pipeline safety. The objectives of the paper were to provide a perspective on safety of pipelines by identifying the principal causes of pipeline accidents, reviewing potential consequences, investigating and reporting on various ways of introducing the likelihood of ruptures and consequences, and recommending an optimal safety enhancement pipeline strategy for the County based on a risk analysis approach. A systematic approach to the evaluation of pipeline safety was made through the use of risk analysis. Practical measures to enhance pipeline safety were developed for both accident prevention and consequence mitigation. Measures were identified in the general areas of information management, regulations, land use, training and education, right-of-way management, emergency response, and pipeline operations including design, construction, and operation. A pipeline safety strategy was recommended based on a systematic approach to risk reduction. |
||||
| P9107 |
EMERGENCY PLANNING FOR CAROLINE SOUR GAS PRODUCTION WELLS,
GATHERING PIPELINES AND GAS PLANT,
SAFETY CASE APPROACH CLIENT: Shell Canada Limited DATE: 1991 DESCRIPTION: In a previous project, PA8820, an emergency risk analysis was carried out on the facilities required to develop a large sour gas reservoir in the Caroline Area of Alberta. Results included a quantification of risks to provide a basis for implementing optimum risk mitigation measures. Included in these measures were impacts associated with emergency response procedures. Consequence scenarios numerically modeled included toxic gas, fire, explosion, pool fire, BLEVE, and fireballs. The present project involved integrating the previous risk analysis work into the planning and implementation of emergency response procedures. Impacts for risk mitigation associated with alternative emergency response procedures were analyzed. Then, results were prepared in order to assist in the meaningful communication of risk and the effects of applying emergency response procedures. Explaining the plans for emergency response was a critical objective of the client because of the significant public involvement. In addition, industry technical, operational, and maintenance personnel and regulatory authorities were also involved in the process of understanding risk and the implications for emergency response plans. |
||||
| P9102 |
LEAK DETECTION IMPACTS ON PIPELINE RISKS
CLIENT: Shell Canada Limited DATE: 1991 DESCRIPTION: A previous project, PA8314, involved the analysis of public risks and consequences of a release of sour gas from a field gathering system. Risks were quantified based on the potential for a full pipeline rupture and the assumption that within 5 minutes of such a rupture, the pipeline pressure sensors would activate line block valves and thereby limit the size of potential release. In a more recent project, PA8820, numerical modeling of pipeline releases included the pressure transient time history, which determines pressure sensor detection capabilities. Calculations proved that leak sizes smaller than a full pipeline rupture may result in greater hazards due to the time response of pipeline pressure sensor detection. The effects of such a scenario on the risks previously estimated for the PA8314 project were assessed in the present project. Results included an analysis of the relative individual risk between a full pipeline rupture and various pipeline leaks. The impact of leak detection directly affected the individual risk results. |
||||
| 1990 | |||||
| P9026 |
ICE
BREAKUP MODELLING FOR NORTHUMBERLAND STRAIT CLIENT: DELCAN/STONE & WEBSTER DATE: 1990/91 DESCRIPTION: The work undertaken in this project was carried out in association with a committee of ice experts to develop predictive models for the influence of the construction of a bridge across Northumberland Strait on the length of the ice season and the characteristics of the breakup season. Two approaches were developed, one based on a correlation between ice volume and the length of the ice season, and the other based on an analytical model of the ice breakup season itself. This latter model included the effects of ice transport, underside decay, and topside decay of the ice cover. The model was developed such that the influence of a bridge could be determined through its effect on transport of ice between zones within the Strait. The model was supported by a comprehensive dataset of wind events, tidal velocities, air temperatures, and solar radiation. The model was hindcast against 20 years of records of breakup seasons in which the model was verified at intervals throughout the season, as well as at the date of last ice. The results of the hindcast analysis were excellent illustrating a very high level of correlation between actual and analyzed results. Using the breakup model as developed, a series of simulations, each involving 1,000 years, was then run for a variety of bridge configurations. For each analysis, the model was executed for the breakup season both with and without the bridge and the difference in dates of last ice used to establish the impact of the bridge upon the length of the ice season in the Strait. The results of these simulations indicated that, on the average, the presence of the bridge tended to accelerate the breakup due to the increased underside melting of ice blocked from passage by the bridge. The extreme results indicated very slight delays in ice-out of the order of one day. |
||||
| P9019 |
RISK ANALYSIS OF ALTERNATE DEVELOPMENT
STRATEGIES FOR A NEW TAR SANDS MINE
CLIENT: Syncrude Canada Ltd. DATE: 1990 DESCRIPTION: Syncrude Canada Ltd. operates an extremely large oil sands mining, extraction and processing operation some forty kilometers north of Fort McMurray, Alberta. In order to maintain or expand current production levels, it will be necessary to open up a new mine and an engineering screening study was carried out to identify, evaluate, and select for subsequent more detailed assessment in the design basis memorandum phase, the most promising integrated mining, transportation, and extraction systems. As part of the engineering screening study, the Bercha Group provided consulting services to develop and implement a risk assessment program. A large number of options or alternative designs were studied, and one of the ranking criteria was to screen high priority options according to risk. The risk assessment program identified and evaluated the major technical, implementation and operational risks associated with each integrated system alternative, in order to determine if any risks were of sufficient magnitude to affect capital and operating cost estimates. A ranking index was developed based on a comparison of the alternative design with that existing in current operations. Results from the risk assessment were included as one of the criteria used to rank the most promising conceptual engineering designs for future mine development. |
||||
| P9018 |
RISK ASSESSMENT SURVEY OF OPERATING FACILITIES
CLIENT: Esso Petroleum Canada DATE: 1990 DESCRIPTION: The client was embarking on a program to promote operational excellence in all of its diverse operating facilities throughout Canada. It was decided to include a preliminary risk assessment survey of all facilities and this project involved the development and presentation of an intensive training program for the client survey team. Technical personnel were recruited from all regional operations and introduced to the program concepts through written materials. All members then met as a team in one location to take an intensive three-day training course and workshop. Following the training session, the Bercha Group provided consulting services for each of the teams as they carried out their surveys. The training workshop began with lectures on risk assessment principles, including definitions and applications. The suite of preliminary risk assessment methods, such as What If analysis and risk logic diagrams, were then presented. Following a review, workshop assignments provided the practical experience necessary to actually undertake the required surveys. Finally a full blown preliminary risk analysis was carried out on an actual facility through role assignments within the classroom setting. |
||||
| P9015 |
RELIABILITY STUDY OF COAL STOCKPILES REQUIRED FOR
ELECTRICAL THERMAL PLANTS CLIENT: TransAlta Utilities DATE: 1990 DESCRIPTION: As the Provincial Regulatory Body, the Public Utility Board questioned the coal stockpile inventory maintained at four thermal plants operated by two utility companies. In essence, costs had to be justified in terms of the risks associated with not supplying the required demand. The reliability of each thermal plant's stockpile was analyzed based on the mining process used to feed each of these stockpiles. The overall process material flow was divided into sequential events which represented the chronology of operations carried out to deliver coal to the stockpile. Operations logic diagrams were derived to assess the sequence of operational events and available contingency action steps should the material flow be interrupted. The impact of each operational problem was characterized by the shortfall in rate at which coal was stockpiled and the length of time of disruption. All significant material flow interruptions were then analyzed in terms of varying levels of contingent action and existing redundancies incorporated in both design and operations. The scope of analysis included the complete cycle from planning through excavation, to stockpiling. |
||||
| P9012 |
ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT FOR PROPOSED EXPANSION OF
THE ALBERTA SPECIAL WASTES
TREATMENT CENTRE CLIENT: Alberta Special Waste Management Corporation DATE: 1990/91 DESCRIPTION: Previous projects, PA8519, PA8420, PA8410, and PA8008 all involved various risk analyses which were carried out for different Government of Alberta departments to support the program being developed to treat hazardous wastes within the province. The above referenced project, PA9012, was a continuation of the previous risk assessment work and was required to support an EIA for a proposed expansion of the existing waste treatment centre. Special or hazardous wastes are collected from generators throughout the province and transported directly or through transfer stations to the treatment centre located in Swan Hills, Alberta. The proposed expansion involved a substantial increase in the volume of hazardous wastes being transported on Alberta roadways and therefore a revised transportation risk assessment was included in the proposal EIA. In addition to the accident and spill analyses, consequence analysis of potential spills of hazardous wastes for both the public and environment were included in the scope of work. Risks associated with the existing operation were compared to those estimated for future operations of an expanded facility. Results from the risk assessment were published in the EIA documents and then were presented and defended during public hearings. |
||||
| P9011 |
RISK ASSESSMENT FOR AN ENVIRONMENTAL CLEAN-UP STUDY OF 21
DEW LINE SITES IN CANADA CLIENT: Canadian Commercial Corporation, on behalf of The United States Air Force DATE: 1990/91 DESCRIPTION: As part of the 1985 agreement between Canada and the United States to modernize the North American Air Defence System, the Dew Line System is being replaced by the North Warning System. An environmental clean-up study of the 21 Dew Line Sites was commissioned in order to identify and investigate areas impacted by past waste disposal and spills and to determine and evaluate alternatives for the disposal of waste and remediation of spill areas. A baseline risk assessment was carried out to document the magnitude of potential health and environmental risks at each of the 21 Dew Line sites and to provide a site specific quantification of risks to provide the basis for developing cleanup strategies. The baseline risk assessment methodology was based on that developed by the U.S. E.P.A. in their Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund. The results of the baseline risk assessment were quantitative and qualitative characterizations of risk based on site specific exposure and toxicity assessments. Both non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic risks were characterized for each contaminant at each site. Non-carcinogenic hazard quotients were estimated to compare the level of site contamination to the potential hazard level. Finally, carcinogenic risk was estimated in terms of the incremental probability of an individual developing cancer over a lifetime as a result of exposure to the site. |
||||
| P9009 |
MOLIKPAQ
MODELLING, PHASE VII, FINAL MODEL TUNING AND VERIFICATION
CLIENT: GULF CANADA RESOURCES LIMITED DATE: 1990 DESCRIPTION: The objectives of this final phase of the development of a non-linear lumped mass model for the Molikpaq involved the verification and final tuning of the model on the basis of a series of actual ice interaction events monitored in 1985 and 1986. Before carrying out the final model tuning, all aspects of the model were thoroughly reviewed to ensure the appropriateness of the various stiffness, mass, and damping values being used. The sensitivity of the model output to various analysis parameters was determined prior to the actual analyses being carried out. The objective of this phase was to carry out a series of analyses of actual events in which only the properties of the ice sheet were varied, reflecting the actual conditions during interaction. The same structural model for the caisson, core, and berm, was used throughout. The results were highly encouraging in that excellent agreement was obtained between analytical and measured values of accelerations and displacements for a variety of locations throughout the structural system. The correspondence between both the period, and the amplitude, of the response was excellent, as was the overall shape of the response. The results indicate that it is possible to develop simple analytical tools capable of modelling complex non-linear dynamics of offshore marine structural systems.
|
||||
| 1989 | |||||
| P8910 |
BRIDGE /
ICE / CLIMATE / FISHERIES INTERACTIONS AND CORRELATIONS -
NORTHUMBERLAND STRAIT CROSSING PROJECT CLIENT: DELCAN/STONE AND WEBSTER JOINT VENTURE DATE: 1989 DESCRIPTION: This project is carried out jointly with Washburn and Gillis, Fredericton, New Brunswick, and P. Lane & Associates, Halifax, Nova Scotia. The project objective is to carry out a series of correlations between a variety of parameters in order to clarify the relationship between the construction of a bridge in Northumberland Strait, the ice climate, the marine and atmospheric climate, and the fishing industry in Northumberland Strait. The project involved the acquisition of information on atmospheric climate, water temperatures, ice regimes, and species landings for five species of fish and shell fish in Northumberland Strait. A series of interactions were carried out to obtain possible correlations between the fish landings and the various physical parameters. In conjunction with the ice jamming model developed in previous studies, these correlations would permit the effect of the bridge to be incorporated into the analysis through perturbations of the ice regime. The project also developed a loop model which related the various physical parameters to the marine food cycle in Northumberland Strait in order to obtain qualitative relationships between the physical parameters and the productivity of the various fisheries. The qualitative loop models were verified against the findings of the various correlations. It was found that the length of the ice season in Northumberland Strait was significantly related to the severity of the ice season and the wind conditions prevailing during the ice clearing period. Further, it was found that, although there was no significant relationship between the severity of the ice season and the cumulative freezing degree days for the region, if the wind regime during the winter was included in the correlation, then the combination of these two independent variables provided an excellent model for the severity of the ice season. |
||||
| P8908 |
CONSULTING
SERVICES AND PUBLIC HEARINGS - NORTHUMBERLAND STRAIT CROSSING
PROJECT CLIENT: DELCAN/STONE AND WEBSTER JOINT VENTURE DATE: 1989 DESCRIPTION: This project involved the provision of expert consultative services to Public Works Canada during the preliminary hearings by the Federal Environmental Assessment Review Panel on the completeness of the data for the environmental assessment of the Northumberland Strait Crossing Project. The project required presence at all of the Public Hearings and the provision of responses to technical questions put by the Review Panel. Further, the project required the provision of consultative services to Public Works Canada and the Delcan/Stone and Webster Joint Venture together with other expert consultants on potential deficiencies in the data as identified by the Panel, and through discussions with the Panel. |
||||
| P8905 |
NORTHUMBERLAND STRAIT RIDGE SURVEY - FIELD PROGRAM AND TEST
PROGRAM CLIENT: DELCAN/STONE AND WEBSTER JOINT VENTURE DATE: 1989 DESCRIPTION: The principal objectives of this project were to obtain certain kinematic and mechanical information on the nature of ridges in Northumberland Strait. The information was required primarily to confirm that interactions between the proposed bridge piers and ridges represented the most significant ice load feature in Northumberland Strait. The work involved a field program in March of 1989 in which a variety of measurements were made on nine ridges with very high sails in Northumberland Strait. These measurements included measurements of ridge heights, depths of consolidation, in situ temperatures, as well as the acquisition of a large sample of ice from the consolidated portion of each ridge. One of the ridges was also surveyed underwater by a team of divers with underwater video. The samples of ice obtained from each ridge were then used for a series of laboratory investigations to determine some of the characteristics of the ice contained in the consolidated layer of each ridge. These tests included strength tests in two orthogonal directions, evaluations of ice density and salinity, as well as crystal structure determinations. The results provided an extremely comprehensive understanding of the kinematic and mechanical characteristics of ridges in Northumberland Strait. It was found that although consolidated depths of up to 1.8 metres were encountered, these layers were not entirely consolidated and significant voids were obtained in all cores. The results of the strength tests indicated that the ice in Northumberland Strait is not unlike first year ice in other regions of the world. The results of this investigation supported the consideration that the parameters being used to determine the ice ridge forces on the bridge piers were not unrealistic and were suitably conservative. |
||||
| 1988 | |||||
| P8827 |
MOLIKPAQ
MODELLING, PHASE V, FREQUENCY ANALYSIS, FILTERING AND DAMPING
EFFECTS CLIENT: GULF CANADA RESOURCES LIMITED DATE: 1988 DESCRIPTION: This project is the fifth phase in a series of projects to develop, test and apply a simple lumped mass model of Gulf Canada's Mobile Arctic Caisson, the Molikpaq. The model has been developed to provide an analytical tool which will readily analyze the interactions between the Molikpaq and an interacting ice floe. These interactions are primarily dynamic and involve complex ice-structure interactions and complex ice behaviour at the interacting face. This project was primarily directed at clearing up a number of outstanding issues which had not yet been addressed and hence verifying the model results by carrying out a series of analyses of actual ice events during 1985 and 1986. During these events, the instrumentation system on the Molikpaq had been used to acquire a considerable amount of data on the response of the system to the interacting ice floes. These responses, mainly the acceleration and displacement responses, were used as the basis of the model verifications. One of the objectives of this current phase was to code a filter system which would duplicate the filtering system inherent to the data acquisition system on the Molikpaq. This analytical filtering system would then permit more realistic comparisons to be made between analytical results and measured responses. A further objective was to provide some realistic measure of the amount of damping available through radiation damping within the plane of the ice sheet. This damping was included in the ice model prior to the comparisons between the measured responses from actual events and the comparable analytical results. Four events were used for comparison purposes, representing a wide range of load frequencies, load amplitudes, and ice properties. A single structural representation was used for all events with only the appropriate ice properties being changed between events. The analyses were carried out for a two node representation of the structure and subsequently for a more complex 25 node representation of the structure. The results were presented in an Interim Report and a Final Report. |
||||
| P8820 |
EMERGENCY RISK ANALYSIS OF CAROLINE SOUR GAS DEVELOPMENT
PROJECT CLIENT: Shell Canada Limited DATE: 1989 DESCRIPTION: The client was proposing to develop a very large sour gas reservoir in the Caroline area of Alberta, which contained natural gas, hydrogen sulphide (H2S), and natural gas liquids. This development was to cover a large region and an accidental release of reservoir fluids represented a potential public hazard due to the toxicity of hydrogen sulphide and the flammability of natural gas liquids. Risk analysis work generally following a Safety Case approach to quantify these hazards was initiated at the earliest engineering phases and was included as an integral part of the development plans through to regulatory approvals. Risks for all principal release scenarios were quantified by integrating the probabilities of releases with information related to release characteristics, plume dispersion, and human response in order to estimate the annual probability of being exposed to a fatal concentration of H2S or an explosive mixture of natural gas liquids. Detailed modelling work was carried out to define risk parameters and provide the basis for implementing optimum risk mitigation measures. These measures were then included in the plans for design, construction, operation and management of the project facilities. The risk analysis work was documented in both technical reports and summaries used for public communications. Expert testimony was provided for an extensive public hearing, which was required for regulatory approval of the development application. Finally, risks were evaluated for a competing application at the hearings, which concluded with regulatory approval going to our client's application. |
||||
| P8819 |
CONSULTING
SERVICES RE: NORTHUMBERLAND STRAIT CLIENT: PUBLIC WORKS CANADA DATE: 1988 DESCRIPTION: The work carried out in this project involved the technical evaluation of the proposals submitted to Public Works Canada in response to the call for tenders for the construction of a fixed link crossing between Prince Edward Island and New Brunswick. The technical evaluations carried out in this project included evaluations to determine the influence of the proposed bridge structure on the ice regime in Northumberland Strait, and the ice forces used for the design of the same bridges. The technical evaluations were carried out on the basis of the requirements of the original bid package and the previous studies carried out by Bercha and Associates on the problem of ice jamming in Northumberland Strait. The review process was a two part process in which each of the tendering consortia were advised of any possible short-comings in their proposal and provided with an opportunity to revise their proposals accordingly. A second round of reviews were then carried out. The review process also considered the impacts that the proposed bridges would have on the fast ice regime in Northumberland Strait, including possible extensions to the fast ice, and any delays in clearing of the fast ice. Although results were submitted to Public Works Canada and the consultants to Public Works Canada on an on-going basis, a Final Report was prepared once the evaluations had been completed. |
||||
| P8811 |
NUMERICAL
MODELLING OF ICE-STRUCTURE INTERACTION RESPONSE OF THE MOLIKPAQ
CLIENT: GULF CANADA RESOURCES LIMITED DATE: 1988 DESCRIPTION: This project was Phase IV of an on-going project to develop a dynamic non-linear lump-mass model of Gulf's Mobile Arctic Caisson, the Molikpaq. This project was essentially an extension of previous work carried out as projects PA8716, PA8704, and PA8609. The principal objective of this project was to integrate into the previously developed lumped mass models for the Molikpaq, a model for the ice sheet. The ice model was based on work carried out by Gulf Canada Resources Limited in conjunction with British Petroleum, to provide a rheological model for the behaviour of the intact ice sheet, and the pulverized ice layer between the ice sheet and the structure. The integration of the ice model was carried out in a series of stages, which included altering the solution technique used with the ice model to accord with that used with the structure model. The structure model consisted of a series of lumped masses connected by elements capable of representing both elastic response and inelastic response. The steel caisson was assumed to behave elastically under all conditions of loading, both static and dynamic, whereas the interface between the caisson and the sand core and berm was provided with a non-linear response capability to model the potential for slip between the caisson and the sand and to model the non-linear behaviour of the sand, particularly shear softening, under dynamic loading. The structure model was also provided with a series of foundation elements which were able to model the interaction between the sand berm and the seabed. The response of the structure model was validated with a series of static ice interactions with the Molikpaq. The ice model consisted of a series of elements which modelled the in-plane elastic behaviour of the ice sheet, the radiation damping within the plane of the ice sheet, and the highly non-linear behaviour of the crushed layer of ice created between the ice sheet and the steel caisson of the Molikpaq. This behaviour included sudden crushing of the intact ice sheet and the creation of pulverized ice, and the viscous extrusion of the pulverized ice under the action of continued motion of the ice sheet which included some cohesive strength. The ice model was analyzed on its own, with a single node representation of the structure, and with a two node representation of the structure. A series of parametric studies were carried out to evaluate the sensitivity of the results to various parameters of the ice model. Finally, the results obtained from the combined model, including a two node representation of the structure, were compared with the data obtained from the prototype measurement system, during an actual ice interaction event. A comparison between the measured and analyzed responses was quite good considering the very simple level of structural modelling being used at this stage. |
||||
| P8807 |
SPECIALIZED NON-LINEAR STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS COMPUTER SOFTWARE
DEVELOPMENT CLIENT: ALBERTA TECHNOLOGY AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS DATE: 1988 DESCRIPTION: This project involved the modification, development, and testing of a series of nine structural engineering programs as marketable software for use on microcomputers. The project was a cost share project, 50% supported by the Alberta Government, and 50% supported by Bercha and Associates. The original programs were available from the University of Calgary where they had been developed as research tools, executable on mainframe computers. Preprocessor programs were developed for each of the nine structural engineering programs to provide user friendly and interactive capability for the input of the required data. Preprocessors included graphic display of the structure, and full edit capability. The programs were fully tested for error checking, admissibility of the data, and for all possible ranges of data combinations. Post processors were developed for each program which permitted the results of the program analysis to be displayed in graphic form both on the screen, and by plotter. User manuals for each of the programs were developed which provided a concise and clear description of the program capabilities, the information required, and provided examples of the application of each program. |
||||
| P8805 |
NORTHUMBERLAND STRAIT CONSULTING SERVICES CLIENT: PUBLIC WORKS CANADA DATE: 1988 DESCRIPTION: For this project, the company was retained by Public Works Canada to act on their behalf in monitoring the acquisition program by McLaren Plansearch to obtain ice, oceanographic, and meteorological data during the winter of 1988 within Northumberland Strait. In this role, the company reviewed the original proposal and made a series of trips to Halifax and Northumberland Strait to view the facilities and hold meetings with McLaren Plansearch personnel on progress of the program. Progress reports were submitted to the project manager with Public Works Canada at regular intervals. |
||||
| P8803 |
NORTHUMBERLAND STRAIT BRIDGE PROBABILISTIC JAMMING ANALYSIS
CLIENT: PUBLIC WORKS CANADA DATE: 1988 DESCRIPTION: The work carried out in this project involved a major extension of the model developed under the previous project, PA8703. This extension involved considerable redevelopment of the jamming model to include effects of consolidation, synergistic effects during the analysis of a single winter, and evaluation of areas of ice blocked. All of these developments were included in the model in a probabilistic fashion in keeping with the entire emphasis of the jamming model. Sensitivity studies were carried out to ascertain the influence of particular ice and bridge structural variables on the amount of ice jammed from which it was determined that the two principal structural variables, span length and pier diameter had an extremely significant effect on the amount of ice jammed. Finally, an analysis was carried out using the most up-to-date information on ice properties in Northumberland Strait, using a six metre diameter pier, with a variety of different span lengths. The results of this analysis indicated that spans in excess of 175 metres would result in acceptably low amounts of ice being jammed. The analysis also determined what effect the ice blocked would have on the length of the breakup season. Analysis was carried out of five breakup seasons for which information was available and it was ascertained that there was a clear relationship between the ice concentration at the beginning of the breakup season and the length of the breakup season itself. Further analysis provided the conclusion that the length of the breakup season was more significantly affected by the environmental conditions during that period of the year. |
||||
| 1987 | |||||
| P8718 |
RISK ASSESSMENT PROGRAM FOR BASIC
ENGINEERING DESIGN OF TARSANDS MINING AND PROCESSING PLANTS MEGA-PROJECT CLIENT: Syncrude Canada Ltd. DATE: 1987 DESCRIPTION: The largest tarsands mining and processing facility in the world is operated by the client some forty kilometres north of Fort McMurray, Alberta. A major expansion project was initiated for this facility and work began with a design basis memorandum describing criteria for the preparation of engineering design specifications. Fourteen consultants from across Canada were then commissioned to provide basic engineering design specifications for major facilities proposed for expansion. Over twenty new facilities and numerous modifications to existing facilities were proposed to develop the mines, install a new energy efficient extraction and froth treatment plant, and integrate new hydroprocessing and hydrotreating plants to improve the yield in quality of synthetic crude oil without increasing sulphur emissions. |
||||
|
P8717 .01 |
INSPECTION
OF MV MISCAROO AND LASER SURVEYS CLIENT: TRANSPORTATION DEVELOPMENT CENTRE DATE: 1988 DESCRIPTION: As an extension to the previous project, this project involved an inspection of the MV Miscaroo while dry-docked in Vancouver in July 1988. The inspection involved a complete survey of the condition of the hull and the acquisition of approximately thirty latex impressions of examples of corrosion of the hull. These impressions were then surveyed using a scanning laser system as well as a mechanical measurement system. The results of the two systems were compared and the results of the entire survey were included in the data base used in the main project, PA8717. This survey of the hull which had been coated with Inerta 160 during the vessel's previous dry-docking in 1985 showed that no significant corrosion had taken place since then. The condition of the coating was excellent. However, the coating was removed in a number of locations and it was found that in the years of operations prior to 1985, significant corrosion had taken place in some locations of the hull. There was also some examples of extreme corrosion at the interface between stainless steel and regular steel on the Kort nozzles. |
||||
| P8717 |
CORROSION
OF MARINE STRUCTURES AND VESSELS OPERATING IN ARCTIC WATERS
CLIENT: TRANSPORTATION DEVELOPMENT CENTRE DATE: 1987 - 1988 DESCRIPTION: The objectives of this study were to provide recommendations and guidelines for operators of steel arctic-going vessels on means of accounting for the severe corrosion that has been experienced to date. The work involved the accessing and analysis of the data base on corrosion acquired by Gulf Canada Resources Ltd. This data base had been acquired from periodic maintenance inspections of Gulf's Beaufort Sea fleet of icebreakers and drilling vessels. The data base also included results obtained from corrosion coupons purposely deployed on vessels in the Beaufort Sea. The data base included the measurement of the manifestations for corrosion as well as all of the required backup information on steel grades, operating history, welding procedures, corrosion protection measures, et cetera. From the analysis of this data, a measure of corrosion severity was established. The general types and severities of corrosion were then used as input to analytical analyses of the residual strength of components of the various vessels. These analyses included the strength of uncorroded sections as well as the strength of corroded sections including the effects of material loss and brittle fracture due to knife edge corrosion particularly of the Heat Affected Zone (HAZ). The comparative strengths of the corroded and uncorroded sections were then used to determine the effect of corrosion on the probability of failure and factors of safety for those components. The results of these analytical studies were then used to formulate guidelines for use in the design, operation, and maintenance of arctic-going vessels based on levels of corrosion and degrees of safety. |
||||
| P8716 |
DEVELOPMENT OF SIMPLE MODEL OF MOBILE ARCTIC CAISSON, MOLIKPAQ -
PHASE III CLIENT: Gulf Canada Corporation DATE: 1987 DESCRIPTION: This project was an extension of work carried out for Gulf Canada Resources Limited under previous projects PE8609 and PE8704. These projects were directed at the development of a methodology and the initial assignment of values to obtain a simple lumped mass model of the Molikpaq, its caisson, core, and berm. The model was designed to permit accurate analytical determination of the response of the structure to ice loads in both static and dynamic modes. In this phase, the 25 node, and 2 node, models previously developed were subjected to a series of sensitivity analyses to tune their responses to applied ice load functions. The sensitivity of the results was determined in some detail and the results tuned against data obtained from the instrumentation system onboard the Molikpaq for actual ice interaction events. Due to the simplicity of the model, the comparisons were only made for responses which were not highly location dependent. Principally, these responses included displacements and accelerations at various points throughout the structural system. The models were tuned for static events, for natural frequencies, and for dynamic response. A detailed analysis of the added mass and damping effects of the water in the ballast tanks of the caisson was undertaken. The Final Report presented the entire findings of the analysis together with appendices indicating the nature of the analytical responses obtained, the dynamic characteristics of the models, and an analysis of the added mass and damping coefficients within the ballast tanks. |
||||
| P8707 |
MOLIKPAQ
ANALYSIS FOR 50-YEAR ICE LOADS CLIENT: Gulf Canada Resources Limited DATE: 1987 DESCRIPTION: For its 1987 deployment, Gulf's Mobile Arctic Caisson, the Molikpaq, was to be set down at lesser water depths than previously, and the sand core was to be consolidated. As a result of these modifications in the deployment of the Molikpaq, concerns were raised regarding the stresses that would occur at various locations within the steel caisson. The work carried out involved static 3-dimensional analyses of the complete caisson with core and berm under the action of the 50-year return period ice forces. The 3-dimensional analysis for the complete structural system was carried out using a non-linear finite element package on a Cyber 205 supercomputer. The software package underwent significant modification to utilize the vector processing capability of the Cyber 205. The analysis was carried out using load increments and non-linear modelling for the interface between the steel caisson and the sand of the core and the berm. In order to simplify the complex structural arrangements of the steel caisson, a series of macro elements was developed in which each macro element encompassed a portion of the caisson between main bulkheads and between horizontal diaphragms. The stiffness of each macro element was developed using a linear elastic finite element program, SPAST, and involved significant finite element modelling in its own right. The results of the large 3-dimensional analyses were used as input to small 2-dimensional finite element models of portions of the caisson structure. The primary concern involved the in-plane stresses within the soil face of the caisson. Stress contours of portions of the soil face were obtained as a result of the two levels of analysis and compared with allowable design conditions. In general, although the calculated stresses were high, it was ascertained that these stresses were not unacceptably high. |
||||
| P8705 |
FINITE
ELEMENT MODELLING OF MOLIKPAQ FOR INSTRUMENTATION ANALYSIS
CLIENT: GULF CANADA CORPORATION DATE: 1987 DESCRIPTION: The work involved the development of a comprehensive three-dimensional finite element model of the Molikpaq including core and berm and the interpretation of the results of a static analysis of the model to identify global load paths. From this interpretation of the results, the proportions of ice load transferred to the core, transferred around the caisson, and transferred to the berm through the caisson base were determined. Subsequently, a detailed finite element analysis of a single bulkhead was carried out in order to permit stresses to be evaluated at points corresponding to the strain gauge locations used as part of the on-board instrumentation package. Comparisons between the results of the finite element analysis and the strain gauge instrumentation were used to further verify the analysis and to test the use of simple algorithms for the interpretation of the strain gauge results and finally, prediction of ice forces. Excellent agreement was obtained between the analytical results and the measured results for some of the strain gauges on each bulkhead, whereas poor results were obtained for other gauge locations. It was determined that the stresses at particular gauge locations were highly sensitive to the vertical location of the ice load on the bulkhead. As this location could only be inferred from the ice load measurement panels on the caisson face, it was concluded that only results from gauge locations at which the stresses were largely insensitive to the vertical location of the ice load should be used for ice load determinations. |
||||
| P8704 |
DEVELOPMENT OF A SIMPLE MODEL FOR THE MOBILE ARCTIC CAISSON,
MOLIKPAQ - PHASE II CLIENT: Gulf Canada Corporation DATE: 1987 DESCRIPTION: This work involved the development of two specific models of the Molikpaq, one extremely simple and one slightly more complex for use with the numerical model developed in Phase I of the project. The work included the assignment of specific values to the various components of each model using only linear analysis, and the verification of the results through comparison with the response measured through the comprehensive instrumentation scheme onboard the Molikpaq. The numerical values were fine-tuned such that accurate values of natural frequencies and static response parameters were obtained by the two levels of modelling. |
||||
| P8703 |
IMPACT OF PROPOSED NORTHUMBERLAND STRAIT CROSSING ON LOCAL ICE REGIME
CLIENT:
PUBLIC WORKS CANADA DATE: 1987 - 1994 |
||||
| 1986 | |||||
| P8609 |
DEVELOPMENT OF SIMPLE MODEL OF MOBILE ARCTIC CAISSON, MOLIKPAQ
CLIENT: GULF CANADA CORPORATION DATE: 1986 DESCRIPTION: The work involved the development of a simple numerical model for non-linear dynamic analysis of Gulf Canada's Mobile Arctic Caisson, the Molikpaq. The model consists of a number of lumped masses in three dimensions connected by a variety of springs and dashpots representing the mass of the caisson, the elastic and inelastic response of the various components of the Molikpaq, and the viscous and hysteretic damping response, respectively. The project included the development of the necessary computer algorithms for the solution of the non-linear dynamic equations of equilibrium utilizing Gulf's HP300 series microcomputer. All components of the algorithm were fully tested through the application of the resulting program to a number of simple models in two and three dimensions utilizing linear, non-linear, static and dynamic analysis. |
||||
| 1985 | |||||
| P8527 |
FINITE
ELEMENT ANALYSIS FOR LOCAL AND GLOBAL ICE LOADS CLIENT: Gulf Canada Resources Inc. DATE: 1985 DESCRIPTION: The work involved the testing of F.G. Bercha and Associates (Alberta) Ltd. ice finite element system through the evaluation of local pressures and global loads on the Molikpaq ice wall during floe impacts. The Molikpaq wall was modelled as a uniformly rigid wall while the ice floe was modelled using both uniform (homogenous) properties and random (inhomogeneous) properties. Various trajectories were considered and a special case of a circular caisson was evaluated. |
||||
| P8526 |
DYNAMIC
MODEL OF THE MOLIKPAQ CLIENT: Gulf Canada Resources Inc. DATE: 1985 DESCRIPTION: The work involved the development of a three-dimensional dynamic model of GCRI's mobile caisson island, the Molikpaq. The model is to be eventually used to analytically determine the effects of ice impacts on the caisson island and to predict the caisson response. The model was developed using three-dimensional macro elements of sections of the steel caisson combined with brick elements representing the core and the berm. The model was tested in static mode, for natural frequencies and under simulated dynamic load and was verified against the instrumentation output obtained by GCRI through the Molikpaq's operating history. |
||||
| P8524 |
ICE SCOUR
METHODOLOGY STUDY CLIENT: Gulf Canada Resources DATE: 1985 DESCRIPTION: The work involved the review, analysis and evaluation of alternate ice scour methodologies directed at optimizing pipeline burial depth within a risk optimization perspective. Following a comprehensive review of all available information, the relevant ice scour parameters were ranked in accordance with their significance. Methodologies were reviewed with respect to parameter completeness, technical acceptability, and definition of uncertainties. Results include definition of alternate methods of approaching a scour problem, generation of comparative results, and final recommendations on the preferred methodology. |
||||
| P8516 |
ICE
INTERACTIONS WITH WINTERIZED AKER D-6 SEMI-SUBMERSIBLE CLIENT: Aker Engineering A/S DATE: 1985 DESCRIPTION: The work involved the determination of ice loads on, and the resulting response of, a specially winterized version of the Aker D-6 semi-submersible designed for operations in marginal ice zones. Marine ice interactions included sheet ice in crushing and flexure modes and rubble pile loads. Static loads and simulated dynamic response loads were evaluated. An advance finite element analysis utilizing state-of-art ice rheology modelling was used in the determination of local pressures on the column shell walls. As the D-6 may operate in berg infested waters, interactions with bergy-bits were evaluated. These included high speed impact pressures on the column shell walls and the evaluation of the effectiveness of a patented bergy-bit deflector. |
||||
| P8513 |
PROBABILISTIC ICE ATLAS FOR CONCEPTUAL DESIGN CLIENT: Marathon Oil DATE: 1985 DESCRIPTION: The work involved the development of a comprehensive ice engineering manual for application in Arctic and marginal ice zone offshore areas. Specifically, the project involved the generation of seasonal ice zone maps for each of the designated study areas, description of the representative ice zones in graphical and tabular format, quantification of kinematic and mechanical properties, definition of data and methodology gaps, calculation of ice loads for all representative structure types for each study area and season, and generation of a final report consisting of an ice atlas and a textual description. The study areas covered included the entire Alaska offshore from the Aleutian Islands throughout the Bering Strait, the Chukchi Sea, around Point Barrow, to the U.S./Canada International Boundary. All ice kinematic and mechanical properties and all resulting ice loads are presented in probabilistic form for return periods of 1 year, 10 years, 30 years and 100 years. |
||||
| P8511 |
AMMONIA STORAGE VESSEL RISK ANALYSIS
CLIENT: Esso Chemical Canada DATE: 1985 DESCRIPTION: The scope of work included an evaluation of potential ammonia releases within the complete manufacturing and distribution system operated by Esso Chemical. Ammonia is a toxic chemical and due to the inventory of material handled by Esso and the geographic distribution of their facilities, there was concern for potential public exposures. A risk analysis was carried out to define the potential risk problem and quantify the risks of potential ammonia losses throughout Alberta and Manitoba. Included in the scope was an analysis of the transportation of ammonia, the fate of releases during transportation, loading, storage, and unloading, and finally, a quantification of the consequences for the affected public. Site specific risk analyses were carried out for the manufacturing facility and a number of field agencies in Alberta and Manitoba. One particular concern included in the detailed analysis was the potential for brittle fracture failures in the storage vessels. The analysis concluded with an assessment of potential risk mitigation measures. |
||||
| P8508 |
RISK ANALYSIS OF PRESSURE VESSEL RUPTURES
CLIENT: Esso Resources Canada Limited DATE: 1985 DESCRIPTION: The work consisted of a systematic analysis of the risk of ruptures due to brittle fracture of pressure vessels. Catastrophic failures of pressure vessels due to brittle fracture occur rarely and the general objective of the work was to present a methodology for quantifying and analysing such rare risks. The risk analysis program included the identification of potential event sequences resulting in a vessel rupture; the development of a fault tree logic structure; the quantification of risks of a vessel rupture and the evaluation of the sensitivity of risk to its major components. Physical property criteria for brittle fracture were utilised as a basis to analyse in detail a specific group of pressure vessels within Esso's operations. |
||||
| P8506 |
ANALYSIS
OF PRESSURE VESSEL RUPTURES CLIENT: Esso Resources Canada Limited DATE: 1985 DESCRIPTION: The work consisted of a systematic analysis of the risk of ruptures due to brittle fracture of pressure vessels. Catastrophic failures of pressure vessels due to brittle fracture occur rarely and the general objective of the work was to present a methodology for quantifying and analyzing such rare risks. The risk analysis program included the identification of potential event sequences resulting in a vessel rupture; the development of a fault tree logic structure; the quantification of risks of a vessel rupture and the evaluation of the sensitivity of risk to its major components. Physical property criteria for brittle fracture were utilized as a basis to analyze in detail a specific group of pressure vessels within Esso's operations. |
||||
| P8504 |
TESTIMONY ON MOBILE PCB DISPOSAL FACILITY
CLIENT: London Occupational Safety and Health Group DATE: 1985 DESCRIPTION: The work involved testimony at the Ontario Ministry of the Environment Hearings on mobile PCB destruction facilities in Ontario. The testimony was based on previous risk analytic work associated with the transportation to treatment of hazardous waste substances and with transportation and storage of PCBs for disposal at a cement plant. Following a brief description on the objectives and methodology of risk analysis, a review of the above-mentioned risk work was presented. Specific comments were then presented on risks associated with mobile PCB disposal operations, which were being reviewed in the hearings for regulatory purposes. |
||||
| 1984 | |||||
| P8417 |
POST-FAILURE ASSESSMENT OF RISK TO WHARF DUE TO ICE LOADING
CLIENT: Department of Public Works - Supply and Services Canada DATE: 1984 DESCRIPTION: The work involved the application of previously documented ice-structure interactions to a wharf in the Baie de Chaleurs off the Gaspe Peninsula which failed in 1973 due to ice encroachment. The work included the interpretation of ten years of ice data for the region from public sources, resulting in probability distribution curves for ice kinematic properties for the site. Local meteorological records were also reviewed. The wharf was structurally analyzed to evaluate failure loads and the two sets of data compared to give the life of the structure and the failure risk. In an additional volume, general approaches to probabilistic ice loads and structural risk were described. |
||||
| P8416 |
LOCAL ICE
PRESSURES IN ICE-STRUCTURE INTERACTIONS CLIENT: Department of Public Works - Government of Canada DATE: 1984 DESCRIPTION: The work involved the development of a refined analytical model to accurately predict local ice pressures. The model incorporated all the known influences on ice rheology and ice-structure interactions. The resulting rheological models were incorporated in a non-linear, finite element program to allow advanced analysis of a variety of ice-structure interactions in both static and dynamic states. The rheology used is completely strain-rate dependent, features both isotropic and planar anisotropic behaviour, and is capable of modelling tension cracking. The resulting coding is fully tested and was supplied with a comprehensive user's manual. The model was used to evaluate ice pressures in interactions between thick uniform ice sheets and vertically sided structures. The modelling included modelling of both the ice sheet and the structure and was carried out using displacement increments until complete plastic flow of the ice sheet occurred. |
||||
| P8415 |
GRAVITY-BASED STRUCTURE OPTIMIZATION FOR ICEBERG IMPACT CLIENT: Northern Construction Company Limited and Delta Marine Consultants B.V. DATE: 1984 DESCRIPTION: The work consisted of preliminary engineering design of gravity-based structures, qualitative and quantitative analysis of GBS-iceberg interactions, and detailed analysis for selected designs. The detailed analysis was carried out utilizing two levels of finite element modelling; the first, a preliminary plane strain model, and the second, an advanced dynamic nonlinear model, giving both global and local pressures. Two specific structure types generated interactively between the FGBAL and construction teams were reviewed in detail and final load calculations carried out utilizing the FGBAL finite element programs. The result was a set of unique structural systems optimized for a Hibernia location in terms of iceberg impact, ocean loading, and operational requirements. |
||||
| P8414 |
AN
INVESTIGATION OF LOCAL ICE PRESSURES ON GRAVITY BASE STRUCTURES
- PHASE II CLIENT: Petro-Canada Resources Inc. DATE: 1984 DESCRIPTION: This project is derived from a requirement by the client to have an understanding of the local contact stresses and the resulting local structure response for various forms of gravity-based structure planned for the Hibernia development. The contact stresses result from iceberg impact and, due to the highly confined nature of the ice at the impact zone, a 3-dimensional finite element development was adopted. As the pressures and forces result from impact, the analysis was also dynamic, resulting in the requirement for a time-dependent solution. The resulting model incorporated both of these characteristics and used a state-of-the-art formulation for the failure of ice in multi-axial stress states. The advanced non-linear iceberg finite element model is based on real time dynamic interaction. All forms of energy dissipation of the initial iceberg kinetic energy, ice deformation and crushing, local structure deformation and global structural deformation are included, as well as advanced material models for rheology. Pre- and post-processors for the finite element package have been prepared. The program was used to carry out a series of analyses on various structural concepts being considered for the gravity base structure for the Hibernia development. For these analyses, the finite element modelling included both the iceberg and portions of the outside wall and the supporting cellular structure. Analyses were carried out on a two-dimensional plane strain model of a horizontal slice of the system. The results of the analysis emphasized the importance of appropriate modelling of the ice but also indicated that the structural stiffness played a secondary but nevertheless significant role in dictating ice contact pressures. |
||||
| P8410 |
RISKS ASSOCIATED WITH THE TRANSPORTATION
TO TREATMENT OF HAZARDOUS WASTE SUBSTANCES CLIENT: Alberta Special Waste Management Corporation DATE: 1984 DESCRIPTION: An analysis was carried out of the risks associated with the truck transportation of liquid hazardous wastes from the various generating sites in Alberta to the proposed Swan Hills treatment plant. The work was an update to a previous risk analysis (P8008) undertaken for the Environmental Council of Alberta. Three scenarios of waste volume distributions were included in the analysis to determine the yearly probability of a spill accident based on 1979, 1980 and 1982 Alberta accident statistics. |
||||
| P8407 |
THE INFLUENCE OF ICE ON THE RELIABILITY OF PRODUCTION
SYSTEMS IN THE HIBERNIA OIL FIELD CLIENT: Petroleum Directorate - Government of Newfoundland and Labrador DATE: 1984 DESCRIPTION: The investigation of the effect of ice on the reliability of proposed Hibernia production systems included identification of ice parameters which are significant determinants of system design criteria and evaluation of the effects on system reliability resulting from uncertain estimates of ice parameters and ice loadings. Risk analytic methodologies were developed and applied in the risk and reliability analysis of an example floating production system. |
||||
| P8401 |
AN
INVESTIGATION OF LOCAL ICE PRESSURES ON GRAVITY BASE STRUCTURES
- PHASE I CLIENT: Petro-Canada Resources Inc. DATE: 1984 DESCRIPTION: The work was directed at the development and application of a preliminary numerical model for the evaluation of local pressures during iceberg-gravity based structure interactions. An extremely comprehensive review of all literature pertinent to icebergs and iceberg-structure interactions in the Hibernia area offshore Newfoundland was carried out. A number of models were developed for kinematically different impacts. These models were used to evaluate the effects of variations of a number of previously identified parameters on interaction loads and pressures. The output was purely deterministic but a sufficiently wide range of parameters and their values were considered to allow detailed conclusions regarding local pressures to be drawn. |
||||
| 1983 | |||||
| P8317 |
ICE-STRUCTURE INTERACTION: ENGINEERING DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION
CRITERIA CLIENT: Department of Public Works - Supply and Services Canada DATE: 1983 DESCRIPTION: The work involved development and compilation of a marine ice load evaluation manual for the determination of total ice loads and ice load distributions on offshore structures with emphasis on gravity-based structures. The work was based on the analytical determination of total ice loads on various types of bottom-founded structures and on the numerical determination of the local peak pressures and their distribution. The numerical analysis was carried out utilizing a non-linear finite element program. Included in the work was an analysis of ice properties, structural parameters, development of interaction theory and generation of representative interaction loads. |
||||
| P8315 |
RISK ASSESSMENT OF TRANSPORTATION SYSTEM FOR SWAN HILLS
AREA MISCIBLE FLOOD CLIENT: Federated Pipe Lines DATE: 1983 DESCRIPTION: An assessment of the risks to human safety as a result of the conversion of an existing oil pipeline to high vapour pressure, natural gas liquid (NGL) service was carried out. Results included fault tree representations of accident scenarios and consequential events, an estimate of the probability of NGL release, presentation of risk spectra showing probabilities associated with potential casualty expectations, assessment of proposed risk mitigation measures and comparison of the proposed pipeline risks with commonplace casualty risks which were familiar to the public. |
||||
| P8311 |
ECONOMIC RISK FROM SOUR GAS WELL DRILLING BLOWOUTS IN ALBERTA CLIENT: Energy Resources Conservation Board DATE: 1983 DESCRIPTION: The work involved an investigation of economic risks as an extension to the previous risk analysis of sour gas drilling blowouts in Alberta described under P8303. Principally, the scope of work was intended to demonstrate the order of magnitude and trend distribution of tractable economic risk. The investigation included analysis of blowout event statistics, definition of physical consequences, classification of damage consequences by severity of blowout, quantification of economic risk and ranking of risk mitigation measures by their benefit-to-cost ratio. |
||||
| P8308 |
RISK ANALYSIS OF DRILLSHIP UNITS OPERATING OFFSHORE
LABRADOR CLIENT: Petroleum Directorate - Government of Newfoundland and Labrador DATE: 1983 DESCRIPTION: A risk analysis of the operations of drillships and dynamically positioned semisubmersibles involved in exploration offshore Labrador was carried out to identify the principal scenarios associated with human, environmental, and property risks. Work included the generation of risk scenarios associated with drilling operations, mobilization and demobilization to and from the drillsite, and ancillary operations supporting the drilling operations. Emphasis was placed on human risks and causal sequences for accident scenarios threatening human safety were analyzed using fault trees. On the basis of the risk analysis, risks were ranked and the risk mitigating effect and implementation costs of specific safety enhancement measures were analyzed. |
||||
| P8306 |
ARCTIC TANKER RISK ANALYSIS - EXTENSION
CLIENT: Canadian Marine Drilling Ltd. DATE: 1983 DESCRIPTION: Certain aspects of a previous risk analysis carried out by FGBAL (P8013) of the proposed crude oil Arctic tanker system were refined and further studied. The work included the development of a probabilistic risk model associated with maneuverability and stopping capabilities of the Arctic tankers as well as detailed sensitivity studies on a number of design modifications, including hull, machinery, navigational hydrocarbon development in the Beaufort Sea, included the risk work on their Environmental Impact Statement and FGBAL personnel defended the risk analysis in the associated hearings. |
||||
| P8304 |
PROGRESS PLANT RISK ANALYSIS CLIENT: Shell Canada Resources Limited DATE: 1983 DESCRIPTION: The work consisted of the generation of a complete risk analysis of principle risk-prone components associated with a particular gas plant project. Specifically, the implementation schedule and associated partnership participation components of the project were isolated and analyzed both independently and interactively. Techniques utilized in the analysis included Delphi, fault tree, and Monte Carlo methods. The emphasis of the risk analysis was on development of applicable decision-making tools and procedures. |
||||
| P8301 |
ICE-STRUCTURE INTERACTION DESIGN MANUAL CLIENT: Amoco Petroleum Company DATE: 1983 DESCRIPTION: The work involved the development of a comprehensive ice engineering manual for application in Arctic and marginal ice zone offshore areas. Specifically, the project involved the generation of seasonal ice zone maps for each of the designated study areas, description of the representative ice zones in graphical and tabular format, quantification of kinematic and mechanical properties, definition of data and methodology gaps, calculation of ice loads for all representative structure types for each study area and season, and generation of a final report consisting of an ice atlas and a textual description. The study areas covered included the entire Alaska offshore from the Aleutian Islands throughout the Bering Strait, the Chukchi Sea, around Point Barrow, to the U.S./Canada International Boundary. |
||||
| 1982 | |||||
| P8218 |
ICE
STRUCTURE INTERACTION CLIENT: Amoco Production Company DATE: 1982 DESCRIPTION: The work consisted of the generation of a comprehensive ice atlas providing probabilistic ice interaction loads for the Alaska offshore continental shelf. Ice kinematic and mechanical properties were assimilated and tabulated for all ice features on the Alaskan OCS from the Aleutian Islands to the Beaufort Sea. Probabilistic ice properties were used to determine probable static ice loads were calculated with sufficient reliability to allow evaluation of costs for Alaska OCS lease sales. |
||||
| P8215 |
ANALYSIS
OF INTERACTIONS OF ICE COVER WITH A SEMI-SUBMERSIBLE DRILLING
UNIT CLIENT: Joint Industry Project: Participants: Texaco, Conoco, Union DATE: 1982 DESCRIPTION: The work included the development of a mathematical model and generation of results for the interaction of ice cover with the columns of a semi-submersible drilling unit operated in marginal ice zone areas. Specifically, the work included state-of-art documentation, environmental and operational parameter definition, theory development, generation of numerical results for representative semi-submersible vessels, and detailed reporting. Extensions of the work included detailed investigation of bridging and non-linear phenomena. Bridging phenomena associated with pile-up formation and sustenance of stable rubble bridges among the columns was investigated utilizing principals of linear and non-linear stability. The effects of non-linear responses of the mooring systems were included in the form of sensitivity coefficients in the linear mooring system response. |
||||
| P8208 |
ICE LOAD
RELIABILITY ANALYSIS SYSTEM CLIENT: Gulf Canada Resources Inc. DATE: 1982 DESCRIPTION: The work involved the development of an ice load risk analysis system applicable to the reliability analysis of offshore structures in ice infested waters. The principal structure type analyzed was a caisson island in moderately deep water at a site in the South Beaufort Sea. The work essentially included the development of failure scenarios leading to risk to capital and operating costs and human life. Following definition of the scenarios, associated structural response probabilistic measures and the associated probabilistic ice loading conditions were quantified. Synthesis involved association of all failure modes, response spectra, and causal spectra through probabilistic fault tree and event tree networks leading to a probabilistic quantification of the reliability of the installation within the Arctic offshore environment. |
||||
| P8201 |
ICE-STRUCTURE INTERACTIONS - ALASKAN OCS CLIENT: Phillips Petroleum Company DATE: 1982 DESCRIPTION: The work involved generation of a reference manual for planning, evaluation, and preliminary design of structures in marine ice-covered waters in selected areas of the offshore continental shelf of Alaska. The work was relatively comprehensive, spanning the definition of ice properties for each of the principal lease areas, calculation of ice loads, and generation of structural concepts for different offshore service conditions. The work included definition of ice properties and associated structural concepts for a range of water depths in lease areas in the South Beaufort Sea, the Chukchi Sea, Norton Basin, Bristol Basin, Navarin Basin, and the St. George Basin. |
||||
| 1981 | |||||
| P8121 |
NORWEGIAN
REFRIGERATED GRAVITY ICE ISLAND CLIENT: Husebye and Olsen DATE: 1981 DESCRIPTION: The work involved coordination and management activities directed at bringing together a viable consortium for the development of a patented system for the generation of ice-reinforced structures applicable to oil exploration in Arctic ice-infested waters. |
||||
| P8118 |
CDU ICE
MANAGEMENT SIMULATION CLIENT: Gulf Canada Resources Inc. DATE: 1981 - 1982 DESCRIPTION: The work involved the development of a predictive Monte Carlo simulator of ice cover and its interaction with an ice management program associated with the operation of the moored conical drilling unit on location in the South Beaufort Sea. The ice cover was rigorously simulated utilizing a hybrid deterministic/Monte Carlo technique which resulted in the generation of continuously varying ice cover representative of various seasonal periods from freeze-up to break-up. Features simulated included pressure ridges, multi-year floes, and ice sheets of various thicknesses. The cover generator was developed on the basis of cumulative distribution functions for the characteristic ice cover parameters obtained by reducing data available from GCRI. The operational component of the simulation involved the Monte Carlo modelling of the cover at a level or condition which the CDU can tolerate. The work included ice cover simulator design, ice management program analysis, and the generation of both sensitivity, predictive, and specific scenario forecast results. |
||||
| P8114 |
ANALYSIS
OF THE NORWEGIAN ICE GRAVITY PLATFORM CLIENT: Aker Engineering A/S DATE: 1981 DESCRIPTION: The work involved the evaluation of the interactions of a special refrigerated structure with the Arctic environment through its construction, installation, and operational phases. Specifically, risk to the structure associated with operational ice loads, with free-floating and seasonally variable ice cover, and with maximum return period ice loads was evaluated. The principal components of the structure are to be constructed on the west coast, and the logistics of a tow around Point Barrow during the ice-free summary window were considered. |
||||
| P8109 |
ICE LOAD
RISK OF SPECIAL ARCTIC DRILL BARGE CLIENT: Gulf Canada Resources Inc. DATE: 1981 DESCRIPTION: The work involved the probabilistic evaluation of interactions through a spectrum of interaction modes associated with dynamic ice cover interacting with a special moored Arctic drill barge. Interactions involving first-year ridges, multi-year ridges, multi-year floes, and level ice were described by means of interaction equations in probabilistic form. Loads associated with a probabilistic severity distribution were generated. The probability of structural survival was then quantified on the basis of cumulative distribution function inputs and scenario fault trees. |
||||
| 1980 | |||||
| P8014 |
A
PROBABILISTIC STUDY OF ICE LOADS ON CAISSON ISLANDS CLIENT: Gulf Canada Resources Ltd. DATE: 1980 DESCRIPTION: The work consisted of a review of statistical analysis of available ice properties in the south Beaufort Sea and their application as inputs to a probabilistic analysis of ice loads on a contemplated Caisson Island in the 60-foot water depth range in that area. The probabilistic analysis was developed on the basis of FGBAL in-house expertise, utilizing the statistical property inputs, and used to generate a series of probabilistic load spectra, including return period considerations, for the full load range scenarios envisioned for the island. |
||||
| P8006 |
GENERAL
ARCTIC RETAINERSHIP CLIENT: Dome Petroleum Limited DATE: 1980 DESCRIPTION: High level technical consultations to Dome in specific areas of Arctic engineering including the following: (a) Optimal offshore structure program development for production structures. (b) Development of ice load instrumentation system for a structure to serve for an exploration platform and as a basis for an instrumented platform giving large-scale ice measurements. (c) Development of optimal ice management program associated with offshore production atoll to permit feasible shipping and logistics operations. (d) Development of optimal Arctic environmental information retrieval system for operational support for exploratory and production operations. |
||||
| P8005 |
ARCTIC
MARINE ICE FIELD SAMPLING, LABORATORY TESTING, AND ANALYSIS
CLIENT: Sohio Petroleum Company DATE: 1980 DESCRIPTION: The work included the recovery of ice blocks from the ice cover in the Prudhoe Bay area in areas adjacent to future drillsites, in locations expected to coincide with C-axis oriented ice. Strategic samples were prepared in the laboratory from the blocks taken in the field, evaluated for crystal orientation utilizing crystallographic methods, and tested for compressive strength at various strain rates and orthogonal directions in order to ascertain the effect of C-axis orientation on strength. A detailed statistical correlation analysis and development of strength functionals was carried out using as a basis the data generated through the program. |
||||
| 1979 | |||||
| P7912 |
ANALYSIS
AND SYNTHESIS OF EXXON CONE TEST DATA CLIENT: Dome Petroleum Limited DATE: 1979 DESCRIPTION: Raw and semi-processed data from a series of small prototype 30° monocone ice interaction tests were reviewed, processed, and applied to the development and verification of certain mathematical models of the interactions. These interactions involved sheets, consolidated ridges, and consolidated and unconsolidated rubble piles. A new mathematical model for the interactions of ice rubble with rigid structures was developed and corroborated with the model test data. Both prototype and full-scale predictions were generated on the basis of the work. |
||||
| P7910 |
LNG
TERMINAL DESIGN FOR ELLEF RINGNES ISLAND - PETRO-CANADA CLIENT: Genstar Construction Limited DATE: 1979 DESCRIPTION: Provision of Arctic expertise to a design consortium for evaluation of alternative LNG terminal schemes to be located at Ellef Ringnes Island. Navigational ice conditions evaluation, ice management at terminal, construction and operational logistics, and preliminary engineering of wharf and terminal structures were included. Ice conditions were obtained from review and interpretation of aerial photomosaics supplemented by black-and-white panchromatic imagery. Several alternate routes and terminal configurations were studied. |
||||
| P7907 |
DESIGN
CRITERIA FOR CAISSON ISLAND PLATFORM SYSTEM CLIENT: Dome Petroleum Limited DATE: 1979 DESCRIPTION: Deep water post-tensioned concrete vertical-sided cylindrical caisson island loadings for governing iceload conditions in the south Beaufort Sea were established. The work involved qualitative review of interactions, design philosophy recommendation, and generation of applicable load spectra for specific structures. |
||||
| P7906 |
STUDY OF
ICE LOADS ON ARTIFICIAL ISLANDS CLIENT: Sohio Petroleum Company DATE: 1979 DESCRIPTION: Establishment of design criteria for artificial islands for hydrocarbon wildcat and production drilling in shallow waters off the Alaskan north coast. Three types of islands were considered; namely, vertical-sided and slope-sided caissons, ice-reinforced gravel, and conventionally reinforced gravel islands. Remote sensing information for three consecutive winters covering the Prudhoe Bay lease area was analyzed to provide a basis for ice kinematics. A variety of ice formations, including sheets, rubble piles, ridges, and ice islands, as well as ice conditions ranging from landfast to dynamic states were considered. Output was in a form amenable to structural designers. |
||||
| P7905 |
EVALUATION
OF ARCTIC PLATFORM SYSTEMS CLIENT: Chicago Bridge and Iron Company DATE: 1979 DESCRIPTION: Provision of specialist consultant services for evaluation of various proprietary structural concepts for offshore structures in Arctic waters. Work involved concept review, calculations, and generation of ice properties and interaction loads for the concepts under consideration. |
||||
| P7903 |
ICE-HULL
DYNAMIC INTERACTION ANALYSIS CLIENT: Melville Shipping Ltd. DATE: 1979 DESCRIPTION: A theoretical and experimental investigation directed at improving predictions of dynamic ice-hull interaction loads generated during ice-breaking transits by Class 7 Arctic LNG carriers through the Northwest Passage. The work emphasized time-dependent nonlinear dynamic Arctic marine ice action on hull, including consideration of scale effects, nonlinear velocity effects on constitutive law, and interaction dynamics. The experimental program included application of high-speed fracture mechanics photography and strain monitoring techniques. |
||||
| 1978 | |||||
| P7825 |
LATERAL
ICE PRESSURE ICEBREAKING RESISTANCE STUDY CLIENT: Melville Shipping Ltd. DATE: 1978 DESCRIPTION: Estimate of the added resistance to icebreaking LNG tanker movement on Arctic route due to wind- and current-induced ice pressure. The work involves the integration of ice pressure effects into the ice-ship interaction equations for a spectrum of conditions likely to be encountered along the route. Review of environmental data, including remote sensing, field sampling, and model test results, ship design parameters, route and schedule constraints was carried out to generate major inputs to the analysis. |
||||
| P7823 |
THERMAL
DISTRIBUTION ICE MANAGEMENT DRILLSHIP CANOPY CLIENT: Canadian Marine Drilling Limited DATE: 1978 DESCRIPTION: Preliminary engineering and logistics design, including structural, mechanical, and naval design and logistics planning for structural canopy to be deployed at perimeter of drillship in order to maintain an ice-free area in the neighbourhood of the drillship during shorefast drilling operations in the south Beaufort Sea. |
||||
| 1977 | |||||
| P7717 |
ARCTIC ICE
CONTROL STRUCTURES SMALL-SCALE PROTOTYPE DESIGN AND SUPERVISION
CLIENT: Canadian Marine Drilling Ltd. DATE: 1977 DESCRIPTION: Certain structural components associated with the small-scale prototype testing of ice control devices to be used in drillships were designed and integrated into an experimental program utilizing a 100 ft. long supply vessel in the Arctic Ocean. Work included design and supervision of portions of the experiment as well as specialist consulting on thermodynamic and ice mechanics aspects of the problems. |
||||
| P7715 |
ARCTIC
SINGLE-POINT MOORING (SPM) SYSTEM CLIENT: Dome Petroleum Limited DATE: 1977 DESCRIPTION: The work entailed the preliminary engineering, logistics, and cost estimates for an offshore Arctic single-point mooring system capable of operating at a water depth of 200 feet. An optimal steel structural form was developed and designed. The system had build into it integrally a quick disconnect capability and integrated ballasting facilities to permit mobility in the case of threat of ice islands. |
||||
| P7712 |
ARCTIC
OFFSHORE LNG TERMINAL CLIENT: Dome Petroleum Limited DATE: 1977 - 1978 DESCRIPTION: Utilization of a steel caisson contained artificial island for the purpose of an LNG plant and storage terminal was investigated. The work involved a preliminary design, logistics, and cost estimates for the construction of the primary island and transfer of a complex LNG barge facility from the ocean surface to a secure location within the island. |
||||
| P7710 |
ARCTIC
MARINE TERMINAL MODULATION CLIENT: Dome Petroleum Limited DATE: 1977 DESCRIPTION: Schedule and cost estimates associated with a feasible modularized construction procedure for Arctic marine terminals suitable for the 50 - 200 foot water depth were generated. A constant storage capacity of 3,000,000 barrels was prescribed. Modifications to previous preliminary designs to facilitate modularization of the ring and tank wall were carried out. The construction procedure evolved about fabrication of the modules in the south, barging of these modules to a sheltered Arctic assembly facility where they would be joined into the ring and tank walls, and a short tow to and installation at the ultimate site. |
||||
| P7709 |
ICE-SHIP
INTERACTIONS EXPERIMENT DESIGN AND MANAGEMENT CLIENT: Canadian Marine Drilling Ltd. DATE: 1977 DESCRIPTION: An analytical and field investigation directed at developing a better understanding of the interaction between a moored ship and stable ice cover was carried out. The analytical work entailed development of a mooring line response simulator, ice-ship interaction theory, and incorporation of the analysis into a computer program which generates mooring line tensions and ship motions for given impinging ice conditions. Numerical sensitivity studies of different eight-point mooring system configurations minimize ice tensions for all probable ice encounter directions. Field corroboration, utilizing a full-scale operating situation for certain parts of the analyses was carried out. Project activities included specialist consulting, experiment design and production of an experimental manual, procurement of equipment, experimental management and supervision, analysis of results, and production of a final report. |
||||
| P7707 |
ARCTIC
MARINE TERMINAL (150 - 200 FT. WATER DEPTH) PRELIMINARY DESIGN
AND LOGISTICS CLIENT: Dome Petroleum Limited DATE: 1977 DESCRIPTION: A preliminary design and order-of-magnitude estimate of costs and schedule for a structural ring-enclosed island type oil storage and marine terminal for 150 and 200 ft. water depths in the Beaufort Sea. A variable storage requirement, from 0 to 3,000,000 barrels of crude oil, was investigated. The terminal can accommodate two million barrel capacity tankers with beams of 170 feet and drafts up to 90 feet. The analysis of the ice-soil-structure interaction carried out for PE7705 above was utilized. Novel forms were necessary in order to counteract the large moments and localized forces imposed upon the terminal structure by prevailing Arctic ice conditions. Conceptual design, cost estimating, and construction logistic aspects of the investigation were carried out in conjunction with appropriately qualified contractors. |
||||
| P7706 |
UNDERWATER
OIL CONTAINMENT VESSEL ANALYSIS INTEGRITY STRESS ANALYSIS
CLIENT: Canadian Marine Drilling Ltd. DATE: 1977 DESCRIPTION: A design for large membrane vessel for containing oil blowout discharges was reviewed and analyzed for the deployment and in-service modes. Work involved the development and solution of submerged inflated membrane equations coupled with the effects of submerged drained sand masses. Practical design considerations were incorporated. |
||||
| P7705 |
ARCTIC
MARINE TERMINAL (50 - 90 FT. WATER DEPTH) PRELIMINARY DESIGN AND
LOGISTICS CLIENT: Dome Petroleum Limited DATE: 1977 DESCRIPTION: A preliminary design and order-of-magnitude estimate of costs and schedule for a structural ring-enclosed island type oil storage and marine terminal for 60 and 90 ft. water depths in the Beaufort Sea. The basic storage requirement for the terminal is three million barrels of crude oil, however sensitivity to different storage capabilities was investigated. The terminal could accommodate two million barrel capacity tankers with beams of 170 feet and drafts up to the full water depth. One of the major problems addressed was the analysis of the soil structure interaction necessary to predict the response to loadings on the outside of the structure caused by various Arctic ice conditions. Conceptual design, cost estimating, and construction logistic aspects of the investigation were carried out in conjunction with appropriately qualified contractors. |
||||
| P7702 |
DEVELOPMENT OF A COMPREHENSIVE THEORY FOR THE PREDICTION OF ICE
FORCES ON CYLINDRICAL AND CONICAL OFFSHORE STRUCTURES CLIENT: Transportation Development Agency DATE: 1977 DESCRIPTION: The development of a comprehensive theory for selecting design ice forces acting on cylindrical and conical offshore structures is carried out utilizing deterministic, semiprobabilistic, and probabilistic analytical techniques and associated computation methods. Flexural and crushing ice sheet failure phenomena are fist described using extensions of customary deterministic theories. Based on the deterministic equations, a semi-probabilistic technique is utilized to investigate the flexure-crushing transitional failure region for which it provides a continuous bimodal transition function. Next, methods of probabilistic design are used to generate a set of probabilistic equations for describing the crushing and flexural interactions. These equations yield values of the mean force and the associated standard deviation, which permits the specification of a unique load spectrum. The probability of an ice load of any given magnitude can easily be obtained from the load spectra. Numerical results include tabulation of loads for both analytically and practically significant ranges of increments of all main interaction variables for all levels and types of analytical methods mentioned above. Salient cases of the tabulations are described and illustrated graphically and applications to current design practices are suggested. |
||||
| 1976 | |||||
| P7619 |
STUDY OF
SCALE EFFECTS OF ICE SHEET FAILURE AGAINST CONICAL OFFSHORE
STRUCTURES CLIENT: Ministry of Transport DATE: 1976 DESCRIPTION: Non-dimensionalization of the flexural ice failure equations. Parametric computer tabulation and graphics to identify trends in the force variables associated with changes in the scale of the interactions as measured by the aspect ratio. Results applicable to design of lighthouse and bridge piers in inland waters. |
||||
|
P7614 .01 |
FEASIBILITY OF USING DRILLSHIP WASTE HEAT FOR MAINTENANCE OF
ICE-FREE AREA AROUND DRILLSHIP CLIENT: Canadian Marine Drilling Ltd. DATE: 1976 DESCRIPTION: One of the conditions necessary to keep a drillship on location in shorefast ice is the prevention of ice formation and impingement in the immediate neighbourhood of the ship. Methods of keeping the ice from forming by utilizing drillship engine exhaust heat were identified and reviewed. Following thermodynamic calculations to ascertain that sufficient heat may be available, several specific schemes for getting the exhaust heat to prevent ice formation were reviewed and evaluated. One of the schemes was selected and preliminary design and cost estimates were carried out. A small-scale prototype test program was developed. |
||||
|
P7614 .02
|
FEASIBILITY STUDY - METHODS FOR MAINTAINING ICE-FREE AREA AROUND
DRILLSHIP CLIENT: Canadian Marine Drilling Ltd. DATE: 1976 DESCRIPTION: A feasibility study of methods of maintaining a 100-foot wide ice-free area around a drillship on location in the South Beaufort Sea was carried out. The methods considered included ones entailing use of structural systems, energy injection systems, and active systems. Among the structural systems considered were the following: (a) Floating structural canopy (b) Air cushion vehicle support canopy (c) Air-supported canopy (d) Air-inflated canopy (e) Structural, air-inflated, or air-supported dome (f) Flexible folding insulation Each of the systems had to have the capability of preventing freezing in a 100 foot wide area around the drillship as well as accommodating peripheral ice movements of up to 80 feet in that area. |
||||
| P7610 |
ENGINEERING PROPERTIES OF ICE IN THE BEAUFORT SEA CLIENT: Dome Petroleum Limited DATE: 1976 DESCRIPTION: The work comprises review, documentation, compilation, and recommendations for the properties of ice in the south Beaufort Sea relevant to ice-structure interaction. Shapes, velocities, strengths, and surface characteristics of the pertinent ice types and formations for various seasonal and geographical zones constitute the major results presented from interpretation and analysis of existing remote sensing information. Geometric and kinematic properties are cast into probabilistic form to optimize use of the relative sparsity of relevant empirical data. Strength and other material properties are presented in mean and maximum ranges to permit realistic use by the designer. The work represents up-to-date compilation of engineering and scientific knowledge of ice properties for the south Beaufort Sea which should augment both the general understanding and state of design readiness of the user relative to offshore oil and gas facilities in the area. A small part of the study area is shown in Figure 1.
|
||||
|
P7602 .01 |
ICE
MECHANICS RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT ICE FORCES ON CONICAL
OFFSHORE STRUCTURES CLIENT: Ministry of Transport DATE: 1976 DESCRIPTION: Extension of work in PE7501 to incorporate alternate failure modes. Computer regeneration of all tables and graphs in metric units. |
||||
| 1975 | |||||
| P7501 |
PARAMETRIC
INVESTIGATION - ICE FORCES ON A CONICAL OFFSHORE STRUCTURE
CLIENT: The Ministry of Transport DATE: 1975 DESCRIPTION: An analytical investigation of the variation in force on a conical offshore structure such as a lighthouse, for a variation of system parameters through a wide range. Parameters varied, including pertinent mechanical ice properties, interface properties, and structure variables. Following the modification of flexural ice sheet failure theory developed by F.G. Bercha earlier, the investigation was carried out with the aid of a digital computer. Over eighty thousand force calculations for approximately forty thousand combinations of the variables were executed. The results were presented in a set of 264 tables and 32 graphs of 8 curves each. Graphics were all performed using the CDC 6400 Computer and CalComp 563 drum plotters. |
This page and all contents are Copyright © Bercha Engineering Limited. Website updated: January 20, 2009